HP ProLiant BL660c HP BladeSystem c-Class architecture - Page 18
Power backplane scalability and reliability, Power and cooling architecture with HP Thermal Logic
 |
View all HP ProLiant BL660c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
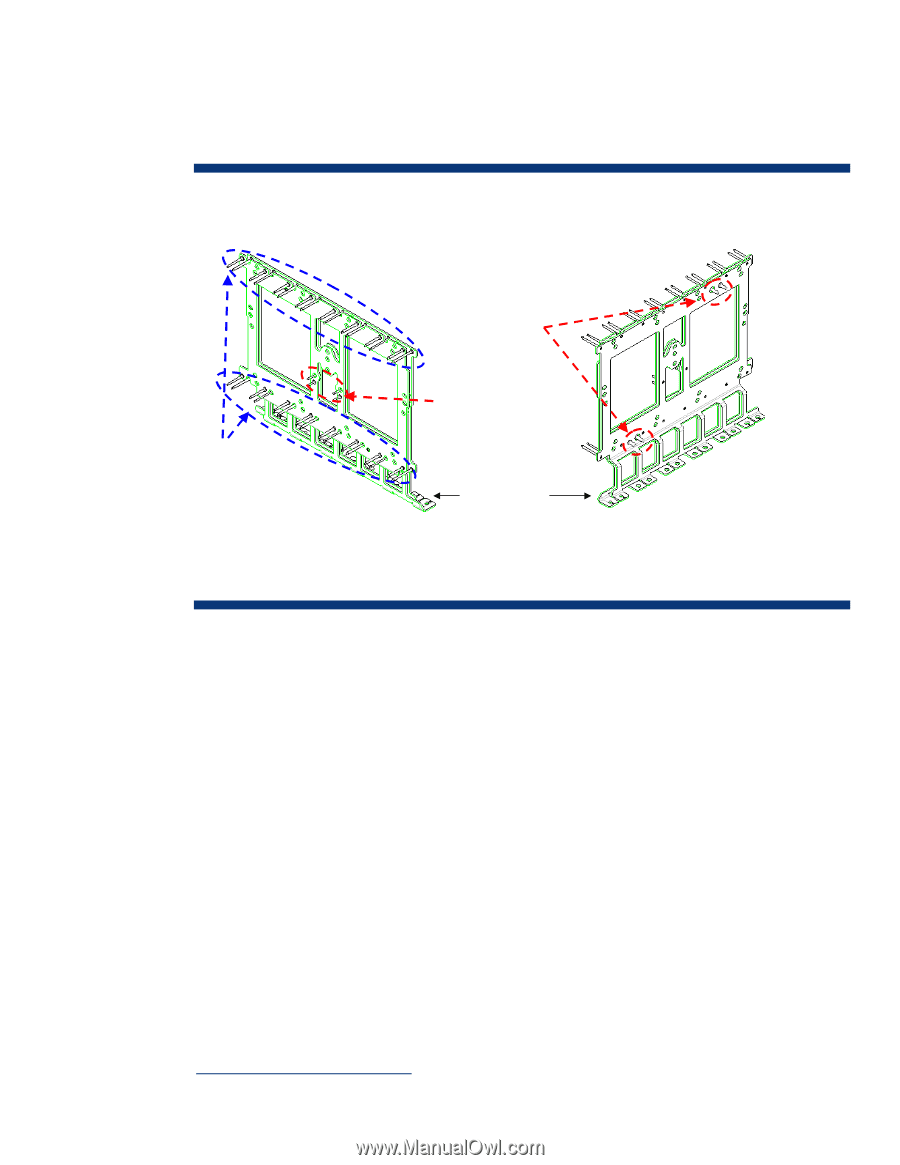
Power backplane scalability and reliability The power backplane is constructed of solid copper plates and integrated power delivery pins to ensure power distribution with minimum losses (Figure 12). Using solid copper plates reduces voltage drops, provides high current density, and high reliability. Figure 12. Sketch of the c-Class power backplane showing the power delivery pins Power delivery pins for the server blades Power delivery pins for the fan modules Power delivery pins for the switch modules Power feet that attach to the power supplies connector board Power and cooling architecture with HP Thermal Logic Power conservation and efficient cooling were key design goals for the BladeSystem c-Class. To achieve these goals, HP consolidated power and cooling resources, while efficiently sharing and managing them within the enclosure. HP uses the term Thermal Logic to refer to the mechanical features and control capabilities throughout the BladeSystem c-Class that enable IT administrators to optimize their power and thermal environments. Thermal Logic encompasses technologies at every level of the c-Class architecture: processors, server blades, Active Cool fans, and the c-Class enclosure. Through the Onboard Administrator controller, IT administrators can access real-time power and temperature data, allowing them to understand their current power and cooling environments. Onboard Administrator allocates power to the device bays based on the specific configuration of each blade in the enclosure. As blades are inserted into the enclosure, the Onboard Administrator discovers each blade and allocates power accordingly, based on actual measured power requirements. Onboard Administrator also allows customers to dynamically and automatically adjust operating conditions to meet their data center requirements. This allows them to maximize performance based on their power and cooling budgets and to forestall expensive power and cooling upgrades. The technology briefs titled "HP BladeSystem c-Class c7000 enclosure technologies" and "HP BladeSystem c-Class c3000 enclosure technologies" give additional information about HP Thermal Logic technologies. Both are available on the HP technology website at www.hp.com/servers/technology. 18