HP ProLiant BL660c HP BladeSystem c-Class architecture - Page 21
Configuration and management technologies, Integrated Lights-out technology, Onboard Administrator
 |
View all HP ProLiant BL660c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
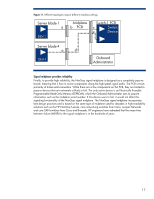
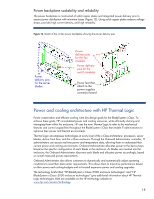
Because the enclosures are designed to include separate physical cooling zones, the Active Cool fans provide cooling for their own zone and redundant cooling for the rest of the enclosure. One or more fans can fail and still leave enough fans to adequately cool the enclosure.6 To ensure scalability, HP designed both the fans and the power supplies with enough capacity to meet the needs of compute, storage, and I/O components well into the future. HP optimizes the cooling capacity across the entire enclosure by optimizing airflow and minimizing leakage through the use of a relatively airtight central plenum, self-sealing louvers surrounding the fans, and automatic shut-off doors surrounding the device bays. Configuration and management technologies One of the goals of the BladeSystem c-Class architecture was to dramatically reduce the amount of time that IT personnel must spend to deploy and manage new systems. To achieve this design goal, HP provided an intelligent infrastructure that makes essential power and cooling information available to administrators and helps automate infrastructure management. Implementing the c-Class Onboard Administrator is the result of these goals. The BladeSystem c-Class architecture also reduces the complexities of switch management in a blade environment. Blade environments provide distinct advantages because their direct backplane connections between switches and blades reduce the number of cables, and therefore cost and complexity. However, early generations of blade environments created the challenge of managing many additional small switches. HP solved this in an innovative way by developing Virtual Connect technology. Virtual Connect technology provides a way to virtualize the server I/O connections to Ethernet or Fibre Channel networks. The technology briefs titled "Managing the HP BladeSystem c-Class" and "HP Virtual Connect technology implementation for the HP BladeSystem c-Class" provide detailed information about these technologies. They are available on the HP technology website: www.hp.com/servers/technology. Integrated Lights-out technology Each ProLiant server blade designed for the BladeSystem c-Class includes an iLO 2 management processor. The iLO 2 processor monitors thermal and operational conditions within each server blade and forwards this information on to the Onboard Administrator. Regardless of a server blade's operating condition, the iLO 2 management processor enables the remote management capabilities that customers have come to expect from ProLiant servers: access to a remote console, virtual media access, virtual power button, and system management information such as hardware health, event logs, and configuration. The iLO 2 device provides a higher-performance remote console (virtual KVM) as well as virtual media functionality that administrators can access from a web browser, command line, or script. The virtual KVM uses an architecture that acquires video directly from the video controller and uses an enhanced compression and refresh technology that reduces the amount of traffic on the network (thereby improving network efficiency). Onboard Administrator Onboard Administrator is a management controller module that resides within the BladeSystem c-Class enclosure. The Onboard Administrator controller communicates with the iLO 2 management processors on each server blade to form the core of the management architecture for BladeSystem c-Class. Customers have the option of installing a second Onboard Administrator board in the c7000 6 The number of fans that can fail depends upon the number of blades, the number of fans, and the location of the blades. The OA reports thermal subsystem status and redundancy level, and will provide alerts when the thermal subsystem status changes. 21