HP Superdome SX2000 Generic Site Preparation Guide, Fourth Edition - Page 22
Humidity Level, ESD Prevention, Humidity Levels Influence the Creation of Static Charges
 |
View all HP Superdome SX2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
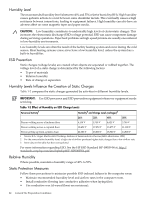
Humidity Level The recommended humidity level is between 40% and 55% relative humidity (RH). High humidity causes galvanic actions to occur between some dissimilar metals. This eventually causes a high resistance between connections, leading to equipment failures. High humidity can also have an adverse affect on some magnetic tapes and paper media. CAUTION: Low humidity contributes to undesirably high levels of electrostatic charges. This increases the electrostatic discharge (ESD) voltage potential. ESD can cause component damage during servicing operations. Paper feed problems on high-speed printers are usually encountered in low-humidity environments. Low humidity levels are often the result of the facility heating system and occur during the cold season. Most heating systems cause air to have a low humidity level, unless the system has a built-in humidifier. ESD Prevention Static charges (voltage levels) are created when objects are separated or rubbed together. The voltage level of a static charge is determined by the following factors: • Types of materials • Relative humidity • Rate of change or separation Humidity Levels Influence the Creation of Static Charges Table 1-2 compares the static charges generated by activities in different humidity levels. IMPORTANT: Use ESD processes and ESD prevention equipment whenever equipment needs servicing. Table 1-2 Effect of Humidity on ESD Charge Levels Personnel Activity1 Humidity2 and Charge Levels (voltages)3 26% 32% 40% 50% Person walking across a linoleum floor 6,150 V 5,750 V 4,625 V 3,700 V Person walking across a carpeted floor 18,450 V 17,250 V 13,875 V 11,100 V Person getting up from a plastic chair 24,600 V 23,000 V 18,500 V 14,800 V 1 Source: B.A. Unger, Electrostatic Discharge Failures of Semiconductor Devices (Bell Laboratories, 1981) 2 For the same relative humidity level, a high rate of airflow produces higher static charges than a low airflow rate. 3 Some data in this table has been extrapolated. For more information regarding ESD, See the HP ESD Standard HP-00005-04 at: http:// standards.corp.hp.com/smc/hpstd/pdf/F-HP0000504.pdf. Relative Humidity Where possible, maintain a humidity range of 40% to 55%. Static Protection Measures Follow these precautions to minimize possible ESD-induced failures in the computer room: • Maintain recommended humidity level and airflow rates in the computer room. • Install conductive flooring (use conductive adhesive when laying tiles). • Use conductive wax (if waxed floors are necessary). 22 General Site Preparation Guidelines