HP Superdome SX2000 Generic Site Preparation Guide, Fourth Edition - Page 23
Acoustics, Facility Characteristics, Floor Loading, Floor Loading Terms - partitions
 |
View all HP Superdome SX2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
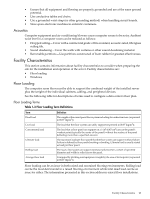
• Ensure that all equipment and flooring are properly grounded and are at the same ground potential. • Use conductive tables and chairs. • Use a grounded wrist strap (or other grounding method) when handling circuit boards. • Store spare electronic modules in antistatic containers. Acoustics Computer equipment and air-conditioning blowers cause computer rooms to be noisy. Ambient noise level in a computer room can be reduced as follows: • Dropped ceiling-Cover with a commercial grade of fire-resistant, acoustic-rated, fiberglass ceiling tile. • Sound deadening-Cover the walls with curtains or other sound-deadening material. • Removable partitions-Use partitions constructed of foam rubber for greatest effectiveness. Facility Characteristics This section contains information about facility characteristics to consider when preparing the site for the installation and operation of the server. Facility characteristics are: • Floor loading • Windows Floor Loading The computer room floor must be able to support the combined weight of the installed server plus the weight of the individual cabinets, cabling, and peripheral devices. See the following table for descriptions of terms used to configure a data center's floor plan. Floor Loading Terms Table 1-3 Floor Loading Term Definitions Term Dead load Live load Concentrated load Ultimate load Rolling load Average floor load Definition The weight of the raised panel floor system including the understructure. (expressed in lb/ft2 (kg/m2)). The load that the floor system can safely support (expressed in lb/ft2 (kg/m2)). The load that a floor panel can support on a 1-in2 (6.45-cm2) area at the panel's weakest point (typically the center of the panel) without the surface of the panel deflecting more than a specified amount. The maximum load (per floor panel) that the floor system can support without failure. Failure is defined by floor panels breaking or bending. Ultimate load is usually stated as load per floor panel. The load a floor panel can support (without failure) when a wheel of specified diameter and width is rolled across the panel. Computed by dividing total equipment weight by the area of its footprint. (expressed in lb/ft2 (kg/m2)). Floor loading can be an issue in both raised and nonraised flooring environments. Rolling load can be the most detrimental in a raised flooring environment while total dead load can be an issue for either. The information presented in this section addresses raised floor installations. Facility Characteristics 23