Sony VGC-RA839G VAIO User Guide - Page 96
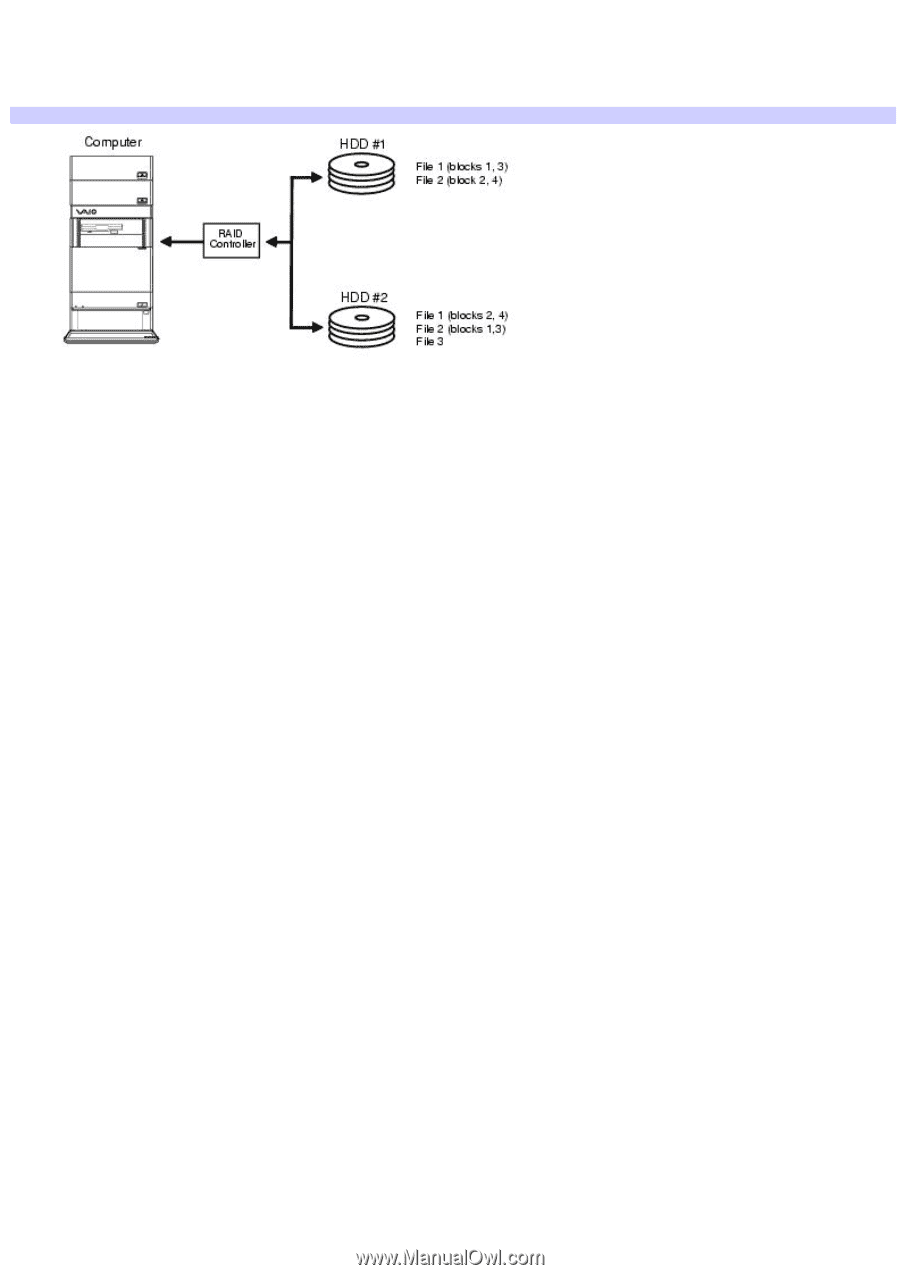
RAID-0, RAID-0: Striping without parity
 |
View all Sony VGC-RA839G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 96 highlights
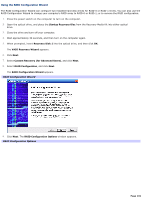
RAID-0 This RAID level uses striping without parity. Striping breaks data into small pieces and then simultaneously writes or reads to multiple locations. This increases your computer's performance and data storage capacity. RAID- 0: Striping without parity Best uses for RAID-0 This RAID level is appropriate for situations where read/write performances is more important than data security. Some examples are environments that use high bandwidth software programs for video production, video editing, or pre-press production. RAID-0 limitations RAID-0 does not provide fault tolerance. All computer data on the array is lost if a single drive in the physical array fails. This RAID level is not a true RAID configuration, as it does not provide redundancy. When using a RAID-0 array, your data storage capacity may be increased, but is limited to twice the size of the smallest hard disk drive in the array. As an example, if your array uses a 60 GB drive and a 20 GB drive, your total hard disk drive volume is 40 GB. The remaining space on the larger drive is not available for use. Page 96