3Com 3824 Implementation Guide - Page 38
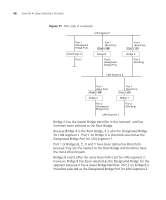
STP Calculation, STP Configuration, Path Cost. Note that the Root Bridge does not have a Root Port.
 |
UPC - 662705467528
View all 3Com 3824 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 38 highlights
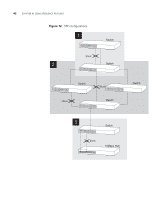
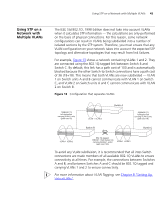
38 CHAPTER 4: USING RESILIENCE FEATURES ■ Each port to have a cost. This specifies the efficiency of each link, usually determined by the bandwidth of the link - the higher the cost, the less efficient the link. Table 4 shows the default port costs for a Switch. Table 4 Default port costs Port Speed 10 Mbps 100 Mbps 1000 Mbps Link Type Half Duplex Full Duplex Aggregated Link Half Duplex Full Duplex Aggregated Link Full Duplex Aggregated Link Path Cost 802.1D, Path Cost 1998 Edition 802.1w-2001 100 2,000,000 95 1,999,999 90 1,000,000 19 200,000 18 199,999 15 100,000 4 20,000 3 10,000 STP Calculation The first stage in the STP process is the calculation stage. During this stage, each bridge on the network transmits BPDUs that allow the system to work out: ■ The identity of the bridge that is to be the Root Bridge. The Root Bridge is the central reference point from which the network is configured. ■ The Root Path Costs for each bridge - that is, the cost of the paths from each bridge to the Root Bridge. ■ The identity of the port on each bridge that is to be the Root Port. The Root Port is the one that is connected to the Root Bridge using the most efficient path, that is, the one that has the lowest Root Path Cost. Note that the Root Bridge does not have a Root Port. ■ The identity of the bridge that is to be the Designated Bridge of each LAN segment. The Designated Bridge is the one that has the lowest Root Path Cost from that segment. Note that if several bridges have the same Root Path Cost, the one with the lowest Bridge Identifier becomes the Designated Bridge. All traffic destined to pass in the direction of the Root Bridge flows through the Designated Bridge. The port on this bridge that connects to the segment is called the Designated Bridge Port. STP Configuration After all the bridges on the network have agreed on the identity of the Root Bridge, and have established the other relevant parameters, each