3Com 3824 Implementation Guide - Page 53
their traffic types are shown in, in order of increasing priority.
 |
UPC - 662705467528
View all 3Com 3824 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 53 highlights
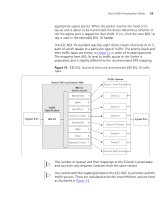
How Traffic Prioritization Works 53 appropriate egress port(s). When the packet reaches the head of its queue and is about to be transmitted the device determines whether or not the egress port is tagged for that VLAN. If it is, then the new 802.1p tag is used in the extended 802.1D header. The IEEE 802.1D standard specifies eight distinct levels of priority (0 to 7), each of which relates to a particular type of traffic. The priority levels and their traffic types are shown in Figure 14 in order of increasing priority. The mapping from 802.1p level to traffic queue in the Switch is proprietary and is slightly different to the recommended IEEE mapping. Figure 14 IEEE 802.1p priority levels and recommended IEEE 802.1D traffic types Ingress Port Switch 3812 and Switch 3824 802.1p Service Levels Background 1 Traffic Classification 802.1D Spare 2 Best Effort 0 Business Critical 3 Multimedia 4 Video 5 Voice 6 Network Control 7 Traffic Queues Queue 1 (Low Priority) Queue 2 Queue 3 Queue 4 Queue 5 (Priority) Queue 6 Queue 7 Egress Port Queue 8 (High Priority) The number of queues and their mappings to the 8 levels is proprietary and can even vary between Switches from the same vendor. You cannot alter the mapping between the IEEE 802.1p priorities and the traffic queues. These are calculated to be the most efficient, and are fixed as illustrated in Figure 14.