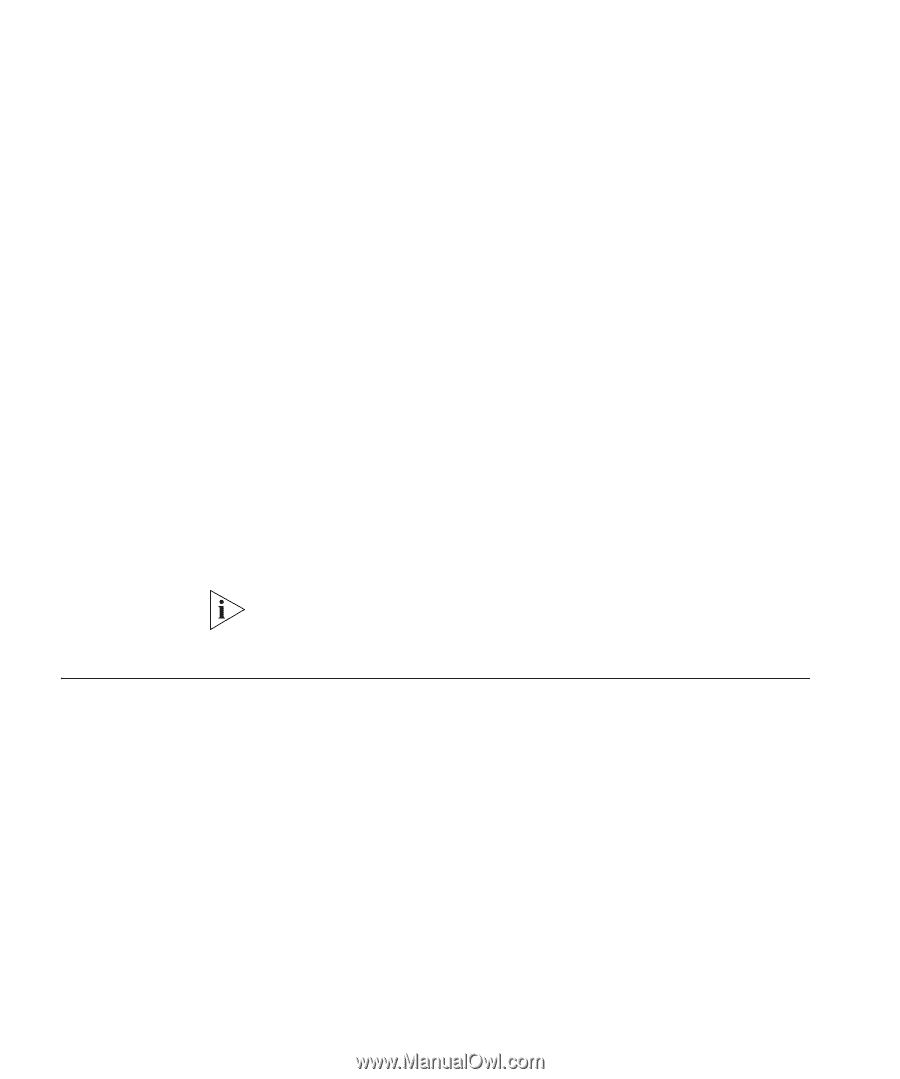3Com 3824 Implementation Guide - Page 56
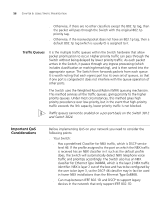
Traffic Queues, Important QoS Considerations
 |
UPC - 662705467528
View all 3Com 3824 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 56 highlights
56 CHAPTER 6: USING TRAFFIC PRIORITIZATION ■ Otherwise, if there are no other classifiers except the 802.1p tag, then the packet will pass through the Switch with the original 802.1p priority tag. ■ Otherwise, if the received packet does not have an 802.1p tag, then a default 802.1p tag (which is usually 0) is assigned to it. Traffic Queues It is the multiple traffic queues within the Switch hardware that allow packet prioritization to occur. Higher priority traffic can pass through the Switch without being delayed by lower priority traffic. As each packet arrives in the Switch, it passes through any ingress processing (which includes classification or marking/remarking), and is then sorted into the appropriate queue. The Switch then forwards packets from each queue. It is worth noting that each egress port has its own set of queues, so that if one port is congested it does not interfere with the queue operation of other ports. The Switch uses the Weighted Round Robin (WRR) queuing mechanism. This method services all the traffic queues, giving priority to the higher priority queues. Under most circumstances, this method gives high priority precedence over low-priority, but in the event that high-priority traffic exceeds the link capacity, lower priority traffic is not blocked. Traffic queues cannot be enabled on a per-port basis on the Switch 3812 and Switch 3824. Important QoS Considerations Before implementing QoS on your network you need to consider the following points: ■ Your Switch: ■ Has a predefined Classifier for NBX traffic, which is DSCP service level 46. If the profile assigned to the port on which the NBX traffic is received has an NBX classifier in it such as the default profile does, the Switch will automatically detect NBX telephone voice traffic and prioritize accordingly. The Switch also has an NBX classifier for Ethernet Type 0x8868, which is the layer 2 NBX traffic identifier. NBX is layer 2 out of the box and has to be configured by the user to be layer 3, so the DSCP 46 classifier may in fact be used in fewer NBX installations than the Ethernet Type 0x8868. ■ Can map between IEEE 802.1D and DSCP to support legacy devices in the network that only support IEEE 802.1D.