3Com 3824 Implementation Guide - Page 52
Traffic Re-Marking, Traffic Prioritization
 |
UPC - 662705467528
View all 3Com 3824 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 52 highlights
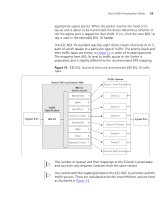
52 CHAPTER 6: USING TRAFFIC PRIORITIZATION uses 64 values that map to user-defined service levels, allowing you to establish more control over network traffic. Advantages of DiffServ over IEEE 802.1D are: ■ No extra tags are required in the packet. ■ DSCP uses the IP header of a packet and therefore priority is preserved across the Internet. ■ DSCP is backward compatible with IPV4 TOS, which allows operation with any existing devices with layer 3 TOS enabled prioritization scheme in use. Traffic Re-Marking Traffic entering the Switch may get downgraded depending on the network policies. If for example a traffic packet enters the Switch with a priority marking higher than the Quality of Service (QoS) configuration polices, the Switch will Re-Mark the packet with a different 802.1D priority or new DSCP value. Traffic Prioritization Your Switch supports Basic and Advanced Quality of Service (QoS) traffic prioritization. Basic traffic prioritization classifies traffic based on layer 2 of the OSI 7 layer model, and the Switch will prioritize the received traffic according to the priority information defined in the received packet. Advanced traffic prioritization can classify traffic at layers 2, 3 and 4 of the OSI 7 layer model. Basic Traffic Prioritization Incoming traffic is classified based upon the IEEE 802.1D frame and is assigned to the appropriate priority queue based upon the IEEE 802.1p service level value defined in that packet. Service level markings (values) are defined in the IEEE 802.1Q 4-byte tag, and therefore traffic will only contain 802.1p priority markings if the network is configured with VLANs and VLAN tagging. The Switch 3812 and Switch 3824 both support basic traffic prioritization. The traffic flow through the Switch is as follows: 1 A packet received by the Switch may or may not have an 802.1p tag associated with it. If it does not, then it is given a default 802.1p tag (which is 0). The packet may be remarked with a new 802.1p value, which will result in all knowledge of the old 802.1p tag being lost. 2 Because the 802.1p priority levels are fixed to the traffic queues (as shown in Figure 14 on page 53), the packet will be placed in the appropriate priority queue, ready for transmission through the