Cisco SLM248G Administration Guide - Page 64
Disable, Blocking, Listening, Learning, Forwarding, Port State, Speed, Path Cost, Default Path Cost
 |
UPC - 745883580279
View all Cisco SLM248G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 64 highlights
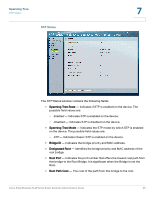
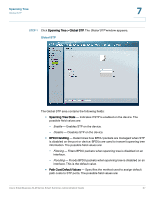
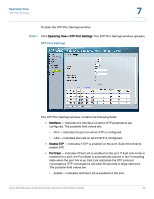
Spanning Tree STP Port Settings 7 - Auto - Port Fast mode is enabled a few seconds after the interface becomes active. - Disable - Indicates that Fast Link is disabled on the port. • Port State - Displays the current STP state of a port. If enabled, the port state determines what forwarding action is taken on traffic. Possible port states are: - Disabled - Indicates that STP is currently disabled on the port. The port forwards traffic while learning MAC addresses. - Blocking - Indicates that the port is currently blocked and cannot forward traffic or learn MAC addresses. Blocking is displayed when STP is enabled. - Listening - Indicates that the port is in Listening mode. The port cannot forward traffic nor can it learn MAC addresses. - Learning - Indicates that the port is in Learning mode. The port cannot forward traffic, however it can learn new MAC addresses. - Forwarding - Indicates that the port is in Forwarding mode. The port can forward traffic and learn new MAC addresses. • Speed - Indicates the speed at which the port is operating. • Path Cost - Indicates the port contribution to the root path cost. The path cost is adjusted to a higher or lower value. Ports with a lower cost are less likely to be blocked if STP detects loops. • Default Path Cost - When checked, returns the port path cost to its default value. • Priority - Priority value of the port. The priority value influences the port choice when a bridge has two ports connected in a loop. The priority value is between 0 -240. The priority value is provided in increments of 16. • Designated Bridge ID - Indicates the bridge priority and the MAC Address of the designated bridge. • Designated Port ID - Indicates the port designated priority and interface. • Designated Cost - Indicates the path cost of the port to the root bridge participating in the STP topology. Ports with a lower cost are less likely to be blocked if STP detects loops. • Forward Transitions - Indicates the number of times the port has changed from the Blocking state to Forwarding state. Cisco Small Business SLM Series Smart Switches Administration Guide 60