Cisco SRST User Guide - Page 7
Convention, Meaning, Description / Comments, Boldface, offset-list, command - configuration example
 |
UPC - 882658171475
View all Cisco SRST manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
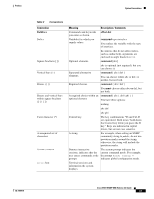
Preface Syntax Conventions Table 2 Conventions Convention Boldface Italics Square brackets ([ ]) Vertical bars ( | ) Braces ({ }) Braces and vertical bars within square brackets ([ { | } ]) Caret character (^) A nonquoted set of characters System prompts Screen font Meaning Description / Comments Commands and keywords offset-list you enter as shown. Variables for which you supply values. command type interface You replace the variable with the type of interface. In contexts that do not allow italics, such as online help, arguments are enclosed in angle brackets (< >). Optional elements. command [abc] abc is optional (not required), but you can choose it. Separated alternative elements. command [ abc | def ] You can choose either abc or def, or neither, but not both. Required choices. command { abc | def } You must choose either abc or def, but not both. A required choice within an command [ abc { def | ghi } ] optional element. You have three options: nothing abc def abc ghi Control key. The key combinations ^D and Ctrl-D are equivalent: Both mean "hold down the Control key while you press the D key." Keys are indicated in capital letters, but are not case sensitive. A string. For example, when setting an SNMP community string to public, do not use quotation marks around the string; otherwise, the string will include the quotation marks. Denotes interactive sessions, indicates that the user enters commands at the prompt. The system prompt indicates the current command mode. For example, the prompt Router (config) # indicates global configuration mode. Terminal sessions and information the system displays. OL-7959-01 Cisco SRST SNMP MIB Release 3.4 Guide vii