HP ProLiant ML110 ProLiant ML110 Generation 2 Server Maintenance and Service G - Page 51
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility, Configuring the power management modes - ram
 |
View all HP ProLiant ML110 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 51 highlights
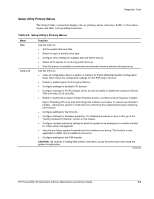
Diagnostic Tools PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility NOTE: For ease of reading, PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility will be simply referred to as "Setup" or "Setup Utility" in this guide. NOTE: The screenshots used in this guide display default system values. These values may not be the same those in your server. PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility is a hardware configuration program built into your system's Basic Input/Output System (BIOS). Since most systems are already properly configured and optimized, there is normally no need to run this utility. You will need to run this utility under the following conditions: • When changing the system configuration including: - Defining the diskette drive - Defining the serial or parallel (COM/LPT) ports to prevent any conflicts - Setting the system time and date - Configuring the hard drives - Specifying the boot device sequence - Configuring the power management modes - Setting up system passwords or making other changes to the security setup • When a configuration error is detected by the system and you are prompted ("Run Setup" message) to make changes to the BIOS settings. NOTE: If you repeatedly receive "Run Setup" messages, the battery may be defective. In this case, the system cannot retain configuration values in CMOS. Ask a qualified technician for assistance. The Setup Utility loads the configuration values in a battery-backed nonvolatile memory called CMOS RAM. This memory area is not part of the system RAM, which allows configuration data to be retained when power is turned off. The values take effect when the system is booted. POST uses these values to configure the hardware. If the values and the actual hardware do not agree, POST generates an error message. You must run this utility to change the BIOS settings from the default or current configuration. 3-2 HP ProLiant ML110 Generation 2 Server Maintenance and Service Guide