HP Rp7410 BSD Sockets Interface Programmer's Guide - Page 126
Field, Description
 |
View all HP Rp7410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 126 highlights
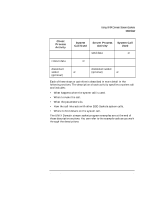
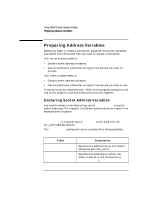
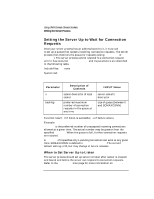
Using UNIX Domain Stream Sockets Preparing Address Variables Preparing Address Variables Before you begin to create a connection, establish the correct variables and collect the information that you need to request a connection. Your server process needs to: • Declare socket address variables. • Get the pathname (character string) for the service you want to provide. Your client process needs to: • Declare socket address variables. • Get the pathname (character string) for the service you want to use. These activities are described next. Refer to the program example at the end of this chapter to see how these activities work together. Declaring Socket Address Variables You need to declare a variable of type struct sockaddr_un to use for socket addresses. For example, the following declarations are used in the example client program: struct sockaddr_un myaddr; /* for local socket address */ struct sockaddr_un peeraddr; /* for peer socket address */ sockaddr_un is a special case of sockaddr and is used with the AF_UNIX address domain . The sockaddr_un address structure consists of the following fields: Field short sun_family u_char sun_path[92] Description Specifies the address family and should always be set to AF_UNIX. Specifies the pathname to which the socket is bound or will be bound (e.g. /tmp/mysocket). 126 Chapter 6