HP Rp7410 BSD Sockets Interface Programmer's Guide - Page 136
Sending Data
 |
View all HP Rp7410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 136 highlights
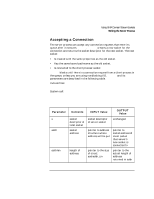
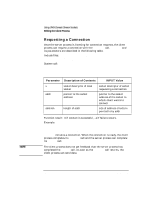
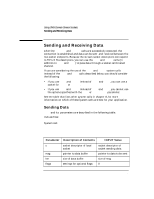
Using UNIX Domain Stream Sockets Sending and Receiving Data Sending and Receiving Data After the connect and accept calls are successfully executed, the connection is established and data can be sent and received between the two socket endpoints. Because the stream socket descriptors correspond to HP-UX file descriptors, you can use the read and write calls (in addition to send and recv) to pass data through a socket-terminated channel. If you are considering the use of the read and write system calls instead of the send and recv calls described below, you should consider the following: • If you use read and write instead of send and recv, you can use a socket for stdin or stdout. • If you use read and write instead of send and recv, you cannot use the options specified with the send or recv flags parameter. See the table that lists other system calls in chapter 8, for more information on which of these system calls are best for your application. Sending Data send and its parameters are described in the following table. Include files: System call: #include #include count = send(s,msg,len,flags) int s; char *msg; int len, flags; Parameter Description of Contents INPUT Value s msg len flags socket descriptor of local socket pointer to data buffer size of data buffer settings for optional flags socket descriptor of socket sending data pointer to data to be sent size of msg 0 136 Chapter 6