HP Rp7410 BSD Sockets Interface Programmer's Guide - Page 90
Parameter, Description of Contents, INPUT Value
 |
View all HP Rp7410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 90 highlights
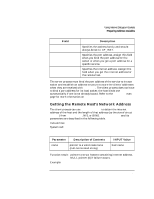
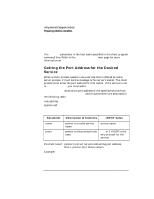
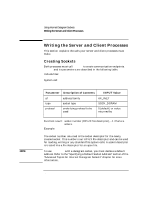
Using Internet Datagram Sockets Preparing Address Variables #include struct hostent *hp; /* point to host info for name server host */ ... servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET; hp = gethostbyname (argv[1]); servaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = ((struct in_addr *)(hp->h_addr))->s_addr; The argv[1] parameter is the host name specified in the client program command line. Refer to the gethostent(3N) man page for more information on gethostbyname. Getting the Port Address for the Desired Service When a client process needs to use a service that is offered by some server process, it must send a message to the server's socket. The client process must know the port address for that socket. If the service is not in /etc/services, you must add it. getservbyname obtains the port address of the specified service from /etc/services. getservbyname and its parameters are described in the following table. Include files: System call: #include struct servent *getservbyname(name, proto) char *name, *proto; Parameter name proto Description of Contents INPUT Value pointer to a valid service name pointer to the protocol to be used service name udp or 0 if UDP is the only protocol for the service Function result: pointer to struct servent containing port address, NULL pointer (0) if failure occurs. Example: #include struct servent *sp; /* pointer to service info */ ... sp = getservbyname ("example", "udp"); servaddr.sin_port = sp->s_port; 90 Chapter 4