HP Rp7410 BSD Sockets Interface Programmer's Guide - Page 29
Overview
 |
View all HP Rp7410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
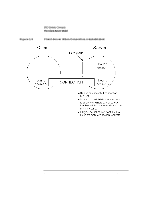
Table 2-1 Using Internet Stream Sockets Overview Overview Internet TCP stream sockets provide bidirectional, reliable, sequenced and unduplicated flow of data without record boundaries. The following table lists the steps involved in creating and terminating a BSD Sockets connection using stream sockets. Creating/Terminating BSD Sockets Connections Using Internet Stream Sockets Client Process Activity System Call Used Server Process Activity System Call Used create a socket bind a socket address (optional) request a connection send data receive data disconnect socket (optional) socket() bind() create a socket bind a socket address connect() listen for incoming connection requests write() or send() accept connection receive data send data read() or recv() shutdown() disconnect socket or close() (optional) socket() bind() listen() accept() read() or recv() write() or send() shutdown() or close() Chapter 2 29