HP Rp7410 BSD Sockets Interface Programmer's Guide - Page 92
Writing the Server and Client Processes
 |
View all HP Rp7410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 92 highlights
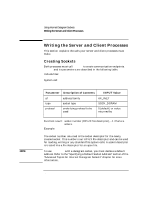
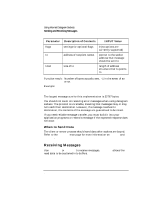
NOTE Using Internet Datagram Sockets Writing the Server and Client Processes Writing the Server and Client Processes This section explains the calls your server and client processes must make. Creating Sockets Both processes must call socket to create communication endpoints. socket and its parameters are described in the following table. Include files: System call: #include #include s = socket(af, type, protocol) int s, af, type, protocol; Parameter Description of Contents INPUT Value af type protocol address family socket type underlying protocol to be used AF_INET SOCK_DGRAM 0 (default) or value returned by getprotobyname Function result: socket number (HP-UX file descriptor), -1 if failure occurs. Example: ls = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); The socket number returned is the socket descriptor for the newly created socket. This number is an HP-UX file descriptor and can be used for reading, writing or any standard file system calls. A socket descriptor is treated like a file descriptor for an open file. To use write(2) with a datagram socket, you must declare a default address. Refer to the "Specifying a Default Socket Address" section of the "Advanced Topics for Internet Datagram Sockets" chapter for more information. 92 Chapter 4