HP Rp7410 BSD Sockets Interface Programmer's Guide - Page 130
Setting the Server Up to Wait for Connection, Requests
 |
View all HP Rp7410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 130 highlights
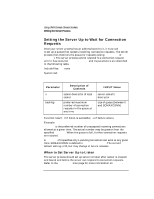
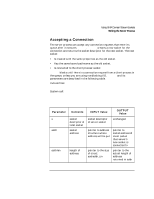
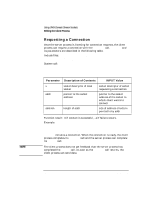
Using UNIX Domain Stream Sockets Writing the Server Process Setting the Server Up to Wait for Connection Requests Once your server process has an address bound to it, it must call listen to set up a queue that accepts incoming connection requests. The server process then monitors the queue for requests (using select(2) or accept ). The server process cannot respond to a connection request until it has executed listen. listen and its parameters are described in the following table. Include files: none System call: listen(s, backlog) int s, backlog; Parameter Description of Contents s backlog socket descriptor of local socket preferred maximum number of connection requests in the queue at any time INPUT Value server socket's descriptor size of queue (between 0 and SOMAXCONN) Function result: 0 if listen is successful, -1 if failure occurs. Example: listen (ls, 5); backlog is the preferred number of unaccepted incoming connections allowed at a given time. The actual number may be greater than the specified backlog. When the queue is full, further connection requests are rejected. A backlog of 0 specifies only 1 pending connection can exist at any given time. SOMAXCONN is defined in . The current default setting is 20, but may change in future releases. When to Set Server Up to Listen The server process should set up server to listen after socket is created and bound and before the server can respond to connection requests. Refer to the listen(2) man page for more information on listen. 130 Chapter 6