HP Rp7410 BSD Sockets Interface Programmer's Guide - Page 44
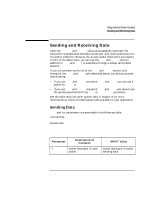
Receiving Data
 |
View all HP Rp7410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 44 highlights
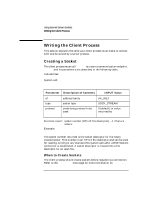
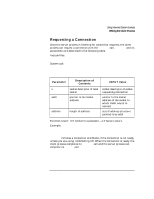
Using Internet Stream Sockets Sending and Receiving Data Parameter Description of Contents msg len flags pointer to data buffer size of data buffer settings for optional flags INPUT Value pointer to data to be sent size of msg 0 or MSG_OOB Function result: number of bytes actually sent, -1 if failure occurs. Example: count = send (s, buf, 10, 0); send blocks until the specified number of bytes have been queued to be sent, unless you are using nonblocking I/O. When to Send Data The server or client process should send data after the connection is established. Refer to the send(2) man page for more information on send. Receiving Data recv and its parameters are described in the following table. Include files: System call: #include #include count = recv(s,buf,len,flags) int s; char *buf; int len, flags; 44 Chapter 2