HP StorageWorks 2/8-EL quickloop fabric assist version 3.0.x user guide - Page 30
Port Level Errors, FL_Port enters OPEN-INIT and becomes the Loop Initialization Master.
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 2/8-EL manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
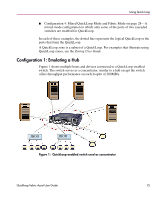
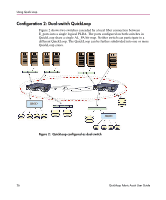
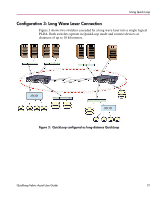
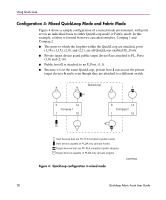
Using Quick Loop If one of the above errors is detected on a switch, the partner reinitializes to form a separate QuickLoop containing only the devices on the partner switch, creating two QuickLoops. If the error condition is removed, the QuickLoops are reinitialized to form a single QuickLoop. If the recovery procedure fails, the switches remain in the single switch QuickLoops, and the procedure is executed again after a time-out period. Port Level Errors The following conditions are considered faulty in regards to the related looplet: ■ Any physical level errors occur, such as loss of synchronization or laser fault. ■ The frequency of LIPs received from a port exceeds a threshold. ■ A port fails to become the Loop Initialization Master within a time-out period after LIPs are either received from or sent to the port. ■ A port does not receive a loop initialization sequence back within a time-out period after the sequence is sent. If an error is detected on a looplet, the QuickLoop is reinitialized with the looplet excluded. The error condition is monitored, and if the condition is removed, the looplet is re-included into the QuickLoop. The looplet error recovery procedure includes the following steps: 1. LIPs are issued to the looplet, and it is determined whether the hidden FL_Port enters OPEN-INIT and becomes the Loop Initialization Master. 2. The rest of the standard Loop Initialization Sequences are completed, and it is determined whether the looplet can be fully initialized within a time-out period. 3. The looplet is kept idle and it is determined whether it remains stable. If the procedure fails at any of the above steps, the looplet remains isolated from the QuickLoop, and the procedure is executed again after the time-out period. If all the steps are successfully completed, the looplet is reinstated into the QuickLoop by full initialization. 30 Quickloop Fabric Assist User Guide