HP StorageWorks 2/8-EL quickloop fabric assist version 3.0.x user guide - Page 33
Fault Isolation and Security, in Using QuickLoop Fabric Assist Mode
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 2/8-EL manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 33 highlights
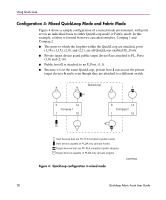
Using QuickLoop Fabric Assist Mode ■ A fabric can have virtually unlimited number of Fabric Assist host loops. ■ A Fabric Assist zone is defined by listing zone members by World Wide Name (WWN) or by fabric port number. If defined with a fazoneCreate telnet command, the private host is identified with "H{ }" notation in its WWN or fabric port designation. If the private host WWN is used, a Fabric Assist zone is automatically configured when that comes online anywhere in the fabric. ■ A Fabric Assist mode private host may or may not be registered in the Name Server, allowing the user to monitor its status. This depends on whether or not the private host responds to the switch's PLOGI request. ■ Fabric Assist mode supports all Zoning features such as Zoning Configurations, Zone Aliases to specify common elements, and fabric-wide distribution. ■ A Fabric Assist zone may be grouped with other zones and placed within various configurations. The Fabric Assist zone telnet commands are described in Using QuickLoop Fabric Assist Mode, Chapter 4. If legacy private hosts or private storage devices have difficulty with U_Port initialization, use the portCfgLport command to configure the port as a loop-only port. Fault Isolation and Security The components of the Fabric Assist mode zone can be specified as either a port address (hard zoning) or as a WWN (soft zoning). If you specify a WWN, the Name Service guarantees that the associated device is automatically configured into the zone wherever it is found in the Fabric. Currently, hard zoning is more secure than soft zoning. The creation of separate Fabric Assist mode zones for each host provides superior fault isolation over emulated loop environments. Quickloop Fabric Assist User Guide 33