HP StorageWorks 2/8-EL quickloop fabric assist version 3.0.x user guide - Page 32
Characteristics and Configuration Guidelines
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 2/8-EL manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
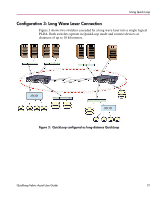
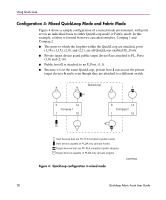
Using QuickLoop Fabric Assist Mode Characteristics and Configuration Guidelines A Fabric Assist mode zone has the following characteristics: ■ Only one Fabric Assist host, an initiator, per Fabric Assist zone is allowed. ■ A Fabric Assist host must be alone on a port; Fabric Assist hosts cannot be located on a hub. ■ Each Fabric Assist mode zone is managed independently, which means multiple private hosts that share storage are not required to participate on the same arbitrated loop. Because each loop is managed separately, loops are isolated from each other. ■ A Fabric Assist mode zone consists of a single private host and at least one target (public or private). The targets can be located anywhere in the fabric. ■ The private host is not constrained by topology restrictions typically imposed by hub or switching hub solutions. A private host has the capability to communicate with a private or public storage device that is located anywhere in the fabric, through the configuration in the Fabric Assist mode zone for the private host. ■ Fabric Assist mode allows private hosts to share storage with public hosts. For example a storage array can be shared between NT and private HP/UX hosts. ■ Private host Loop Initialization Primitives (LIPs) do not interact with public storage devices. ■ With Fabric Assist mode, private hosts can access a combination of public or private (FC-AL) storage devices. A storage device may be simultaneously accessible by either private hosts with Fabric Assist or public hosts with standard zoning. ■ Each switch can support up to 125 distinct devices assigned to private hosts connected to that switch. The target limit per switch is 125. If you try to zone more than 125 targets with Fabric Assist hosts on one switch, the switch will be unable to allocate a phantom for itself and will be unable to probe private targets. This means the private targets will not be listed in the name server database, and public hosts will not be able to talk to these private targets. ■ A storage device (public or private target) can be configured into multiple Fabric Assist zones. ■ Each virtual loop has a separate AL_PA (Arbitrated Loop Physical Address) domain. Each storage device is assigned a phantom AL_PA on a Fabric Assist zone. (The same device may be accessed by a different phantom AL_PA from the private host of a different Fabric Assist zone.) 32 Quickloop Fabric Assist User Guide