Lexmark C540 Service Manual - Page 123
Theory of operation, Print engine theory
 |
View all Lexmark C540 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 123 highlights
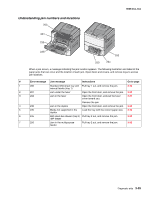
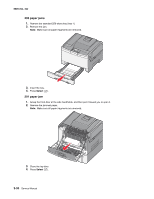
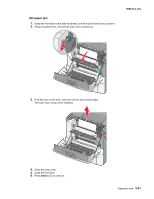
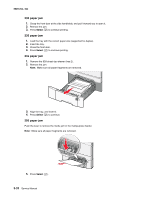
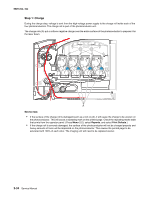
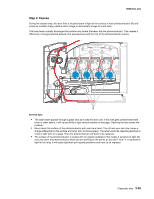
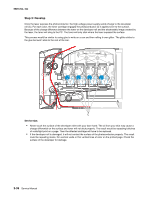
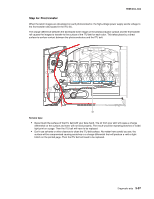
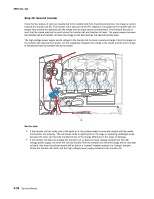
5025-2xx, 4xx Theory of operation Print engine theory Electrophotographic process (EP process) The method that all laser and LED printers use to print is called the electrophotographic process. These machines use differences in charge to manipulate and move toner from the toner cartridge to the printed page. Even though the basic EP process is the same for every laser and LED printer, the specifics for each printer are different. Electrophotographic process basics This printer is a single laser printer that uses four toner cartridges (cyan, yellow, magenta and black) to create text and images on media. The printer has four photoconductors (called a photodeveloper cartridge or PC unit) and an image transfer unit (ITU). Each color toner is painted to it's respective photoconductor at the same time. The transfer belt passes under the four photoconductors and the four color image is produced and transferred to the media in one pass. During the printing process, the printer follows the six basic EP process steps to create its output to the page. These six steps are: 1. Charge the photoconductor (PC unit) 2. Expose the photoconductor (PC unit) 3. Develop the toner on the photoconductor (PC unit) 4. First and second transfer of toner to the ITU and then to the media. 5. Fuse the toner to the media 6. Clean/erase the photoconductor and the ITU. In summary, the printer's controller board receives print data and the command to print. The controller board then initiates the print process. The controller board is the command center for the EP process and coordinates the various motors and signals. The high-voltage power supply sends charge to various components in the EP process. The laser fires on the photoconductors and alters the surface charge relative to the planned image for each photoconductor. Each photoconductor rotates past its respective developer roll and toner is developed on the surface of each photoconductor. The four separate color images are then transferred to the transfer belt on the ITU as it passes under the photoconductors. After the image is transferred to the transfer belt the photoconductors are cleaned and recharged. The transfer belt, carries the four-colored image towards the transfer roll. Media is picked up from the tray and carried to the transfer roll where the image is transferred from the transfer belt to the media. The timing of the paper pick is determined by the speed of the transfer belt. The media is carried to the fuser rollers where heat and pressure are applied to the page to permanently bond the toner to the page. The fuser rollers push the media into the output bin. The transfer unit is cleaned and the process begins again for the next page. Diagnostic aids 3-33