McAfee VCLCDE-AA-DA Product Guide - Page 30
Response and notification options, Table 3-3
 |
View all McAfee VCLCDE-AA-DA manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
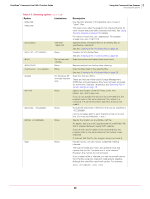
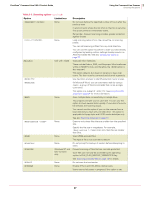
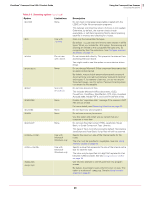
VirusScan® Command Line 5.20.0 Product Guide 3 Using the Command-Line Scanner Choosing the options Response and notification options The response and notification options determine how the scanner responds to an infection. You can use a combination of these options to customize the scan. None of the options in the following table occur automatically. To activate each option, specify it in the command line. Table 3-3 Response and notification options Option Limitations /CLEAN None. /CONTACTFILE None. /DAM /DEL None. None. /EVLOG /LOCK On Windows NT and later versions. In MS-DOS systems only, not Windows NT or later. Description Automatically remove any infections. By default, the program states only that infections were found but does not try to clean the infected files. If the program cannot clean the file, it displays a warning message. If you use this option, repeat the scan to ensure that there are no more infections. See If the scanner detects a virus on page 40 for more information. Display the contents of the specified file when a virus is found. This enables you to provide contact information and instructions to the user when a virus is encountered. We recommend using /LOCK with this option. This option is especially useful for networks, because you can maintain the message text in a central file, rather than on each workstation. Any character is valid in a contact message except a backslash (\). Messages beginning with a slash (/)or a hyphen (-) must be placed in quotation marks. Delete all macros in a file if an infected macro is found. If you suspect you have an infection in your file, you can choose to remove all macros from the file to prevent any exposure to a virus. To pre-emptively delete all macros in a file, use this option with /FAM, although this should be used with caution. If you use these two options together, all found macros are deleted, regardless of the presence of an infection. Delete infected .COM and .EXE files. This option does not delete infected items within Microsoft Word documents or archives. If the scanner detects infected files within an archive, it does not delete the files within the archive, nor does it delete the archive itself. We recommend that you use the /CLEAN option to protect against viruses that infect file types other than .COM or .EXE. See If the scanner detects a virus on page 40 for more information. Use Event Logging. Any detections are recorded in the Application Log of the Event Viewer. Halt and lock the computer if a virus is found. This option is appropriate in vulnerable network environments, such as open-use computer laboratories. We recommend that you use this option with the /CONTACTFILE option to tell users what to do or whom to contact if the scanner locks their computer. 30