Netgear WNR2000v2 WNR2000 User Manual - Page 70
Using a Dynamic DNS Service, Dynamic DNS
 |
View all Netgear WNR2000v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 70 highlights
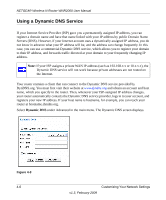
NETGEAR Wireless-N Router WNR2000 User Manual Using a Dynamic DNS Service If your Internet Service Provider (ISP) gave you a permanently assigned IP address, you can register a domain name and have that name linked with your IP address by public Domain Name Servers (DNS). However, if your Internet account uses a dynamically assigned IP address, you do not know in advance what your IP address will be, and the address can change frequently. In this case, you can use a commercial Dynamic DNS service, which allows you to register your domain to their IP address, and forwards traffic directed at your domain to your frequently changing IP address. Note: If your ISP assigns a private WAN IP address (such as 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x), the Dynamic DNS service will not work because private addresses are not routed on the Internet. Your router contains a client that can connect to the Dynamic DNS service provided by DynDNS.org. You must first visit their website at www.dyndns.org and obtain an account and host name, which you specify in the router. Then, whenever your ISP-assigned IP address changes, your router automatically contacts the Dynamic DNS service provider, logs in to your account, and registers your new IP address. If your host name is hostname, for example, you can reach your router at hostname.dyndns.org. Select Dynamic DNS under Advanced in the main menu. The Dynamic DNS screen displays. Figure 4-3 4-6 Customizing Your Network Settings v1.3, February 2009