Ricoh Aficio SP C820DNT1 Design Guide - Page 22
In the case of Windows Authentication, NTLMv1 Authentication or Kerberos Authentication is
 |
View all Ricoh Aficio SP C820DNT1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
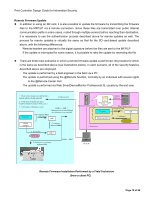
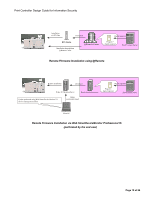
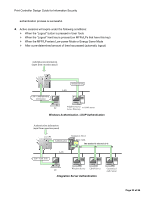
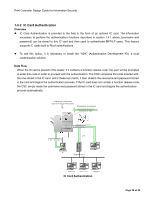
Print Controller Design Guide for Information Security in the MFP/LP. The communication path can be encrypted using SSL, however for environments that do not support SSL protocol, the password itself is encrypted using an encryption key specified by the Administrator. To do this, however, the Printer/Scanner option must be installed.To protect against brute force password cracks and DoS attacks via repeated login, the MFP/LP is capable of detecting a high frequency of illegal login requests. Administrators can view the detection results by accessing the job log, or by checking the notification e-mail sent to them. Also, for any consecutive failed authentication attempts, the MFP/LP will delay its response. It is possible to set the MFP/LP to automatically lock out any user if the number of failed login attempts by that user exceeds the predetermined limit (access is denied and further usage of that account is prohibited). Additionally, when the operator registers their authentication password, the MFP/LP checks the format against the password policy. This policy is set by the Administrator using the following parameters: Minimum length: Can be set to a value from 1- 32 characters Complexity: Can be set to "Level 1", "Level 2", or "Off" Level 1 requires that the password contain two or more of the following types of characters, while Level 2 requires that the password contain three or more types: English capital letters, English lower-case letters, numbers, symbols. Note: These two features apply to general user accounts authenticated through Basic Authentication (performed by the MFP/LP), and to Administrator accounts authenticated through all authentication modes. When users log in via an external server, instead of performing the password policy check described above, the MFP/LP follows the authentication results received from the server. The information for performing the authentication of administrators is encrypted and then stored in the MFP/LP in non-volatile memory. Therefore, it is always possible to perform authentication on administrators even when a failure occurs with the MFP/LP HDD or one or more of the external authentication servers is down. In the case of Windows Authentication, NTLMv1 Authentication or Kerberos Authentication is performed with the specified domain controller, after which an attempt is made to establish an LDAP connection with the active directory. The e-mail address, FAX number and GUID are then obtained for users who successfully clear the authentication. The same NTLM Authentication process is performed for LDAP Authentication as well, after which an LDAP search is performed to obtain the user's e-mail address, FAX number and GUID. Kerberos Authentication can be used for LDAP Authentication and LDAP searches. Kerberos Authentication tickets are not stored in non-volatile memory, and are destroyed as soon as the Page 22 of 86