TRENDnet TEW-824DRU User's Guide - Page 31
Advanced Settings
 |
View all TRENDnet TEW-824DRU manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
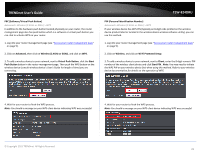
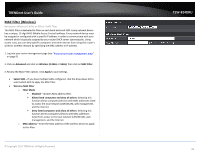
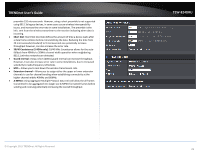
TRENDnet User's Guide Please refer to page 21 to find out about different security types and page 22 for wireless security configuration. The diagram shows an example of a client connecting to SSID 1 and another client connecting to SSID 2. 5. To save changes, click Apply. Note: If you would like to discard the changes, click Cancel before you click Save. Note: You can repeat the steps to enable and configure additional SSIDs. © Copyright 2015 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved. TEW-824DRU Advanced Settings Advanced > Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz) > Advanced These settings are advanced options that can be configured to change advanced wireless broadcast specifications. It is recommended that these settings remain set to their default values unless you are knowledgeable about the effects of changing these values. Changing these settings incorrectly can degrade performance. Beacon Period: A beacon is a management frame used in wireless networks that transmitted periodically to announce the presence and provide information about the router's wireless network. The interval is the amount time between each beacon transmission. Default Value: 100 milliseconds (range: 100-1000) DTIM: A DTIM is a countdown informing clients of the next window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages. When the wireless router has buffered broadcast or multicast messages for associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value. Wireless clients detect the beacons and awaken to receive the broadcast and multicast messages. The default value is 1. Valid settings are between 1 and 255. Fragment Threshold: Wireless frames can be divided into smaller units (fragments) to improve performance in the presence of RF interference and at the limits of RF coverage. Fragmentation will occur when frame size in bytes is greater than the Fragmentation Threshold. This setting should remain at its default value of 2346 bytes. Setting the Fragmentation value too low may result in poor performance. RTS Threshold: The Request To Send (RTS) function is part of the networking protocol. A wireless device that needs to send data will send a RTS before sending the data in question. The destination wireless device will send a response called Clear to Send (CTS). The RTS Threshold defines the smallest data packet size allowed to initiate the RTS/CTS function. Default Value: 2347 (range: 1-2347) TX Power: This setting allows you to adjust the wireless transmit power to a lower setting. In busy wireless environments, lowering the transmit power may improve better performance and connectivity and decrease interference with neighboring wireless networks. Short Preamble: Using a short preamble can potentially increase throughput as the transfer time is 96 microseconds versus the more commonly used long 28