Dynex DX-wegrtr User Manual (English) - Page 53
Limiting the Wireless Transmit Rate
 |
UPC - 600603114403
View all Dynex DX-wegrtr manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 53 highlights
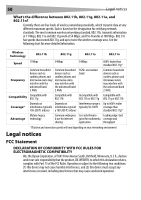
Troubleshooting 53 Problem: I can't connect to the Internet wirelessly, and my network name is not listed. Solution: If the correct network name is not listed under Available Networks in the wireless configuration utility, please attempt the following troubleshooting steps: 1. Temporarily move your computer, if possible, 5 to 10 feet away from the router. Close the wireless configuration utility, and reopen it. If the correct network name now appears under Available Networks, you may have a range or interference problem. See the suggestions discussed in "Placement of your router for optimal performance" on page 47. 2. Using a computer that is connected to the router through a network cable (as opposed to wirelessly), make sure that Broadcast SSID is enabled. This setting is found on the router's wireless Channel and SSID configuration page. Problem: My wireless network performance is inconsistent. Data transfer is sometimes slow. Signal strength is poor. I am having difficulty establishing and/or maintaining a Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection. Solution: Wireless technology is radio-based, which means connectivity and the throughput performance between devices decreases when the distance between devices increases. Other factors that will cause signal degradation (metal is generally the worst culprit) are obstructions such as walls and metal appliances. As a result, the typical indoor range of your wireless devices will be between 100 to 200 feet. Note also that connection speed may decrease as you move farther away from the router or access point. In order to determine if wireless issues are related to range, we suggest temporarily moving the computer, if possible, five to 10 feet away from the router. Changing the Wireless Channel Depending on local wireless traffic and interference, switching the wireless channel of your network can improve performance and reliability. The default channel the router is shipped with is channel 11. You may choose from several other channels depending on your region (see "Changing the Wireless Channel" on page 25 for instructions on how to choose other channels). Limiting the Wireless Transmit Rate Limiting the wireless transmit rate can help improve the maximum wireless range, and connection stability. Most wireless cards have the ability to limit the transmission rate. To change this property, go to the Windows Control Panel, open Network Connections and double-click on your wireless card's connection. In the Properties dialog box, select the Configure button on the General tab (Windows 98 users will have to select the wireless card in the list box and then click Properties), then choose the Advanced tab and select the rate property. Wireless client cards are usually set to automatically adjust the wireless transmit rate for you, but doing so can cause periodic disconnects when the wireless signal is too weak; as a rule, slower transmission rates are more stable. Experiment with different connection rates until you find the best one for your environment; note that all available transmission rates should be acceptable for browsing the Internet. For more assistance, see your wireless card's user manual.