HP Dc7700 Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) on HP Compaq dc7700 and - Page 3
Introduction, Basics of RAID Technology - desktop pc
 |
UPC - 882780715318
View all HP Dc7700 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
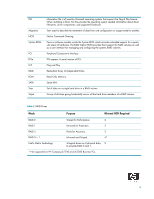
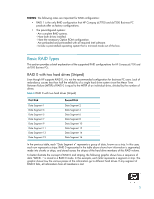
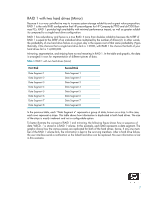
Introduction RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a category of hard drives that employ two or more drives in combination for fault tolerance and performance. Initially used with servers, desktop PCs are increasingly using RAID by adding a RAID controller and extra IDE or SCSI disks. Newer system boards often have RAID controllers. RAID technology takes advantage of Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) and the integration of RAID into the Intel Q965/ICH8-D0 chipset. The HP Compaq dc7700 and dx7300 Business PC products are the first business desktops to incorporate RAID drive support through factory configurations. This white paper provides a basic overview of RAID technology, supported factory configurations of HP Compaq dc7700/dx7300 Business PCs, other supported RAID configurations, and basic instructions on how to migrate non-RAID to RAID configurations in the field. Mirroring and Parity Fault tolerance is achieved by mirroring or parity. Mirroring is 100% duplication of the data on two drives (RAID 1). Parity is used to calculate the data in two drives and store the results on a third drive (RAID 5). After a failed drive is replaced, the RAID controller automatically rebuilds the lost data from the other two drives. RAID systems may have a spare drive (hot spare) ready and waiting to be the replacement for a drive that fails. Disk Striping RAID improves performance by disk striping, which interleaves bytes or groups of bytes across multiple drives, so more than one disk is reading and writing simultaneously. Basics of RAID Technology Definitions Table 1 Basic RAID Definitions ATA BIOS Chipset HDD ICH IDE Advanced Technology Attachment. Basic Input/Output System, also known as system ROM. Term used to define a collection of integrated components required to make a PC function. Hard disk drive. Intel Input/Output Controller Hub, inside this component resides the mass storage controller. ICH is part of the Intel Q965 chipset. Integrated Drive Electronics. 3