HP Dc7700 Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) on HP Compaq dc7700 and - Page 8
RAID 5 with three hard drives
 |
UPC - 882780715318
View all HP Dc7700 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
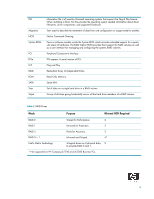
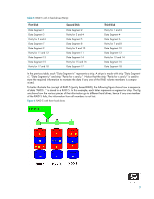
Figure 3 Reliability: RAID 1 - Mirroring RAID 5 with three hard drives RAID 5 has been used in servers for many years and is one of the most common types of RAID. RAID 5 uses striping with parity data in distributed blocks across all member disks. Therefore, the mass storage controller can simultaneously write new information to two hard drives and parity information to the third hard drive, so if one hard drive fails, the RAID controller can rebuild all the information after the volume degradation occurred. Hence, RAID 5 with three hard drives has similar performance to RAID 0 with two hard drives, and the reliability of RAID 1 with a minimum of three hard drives. 8
8
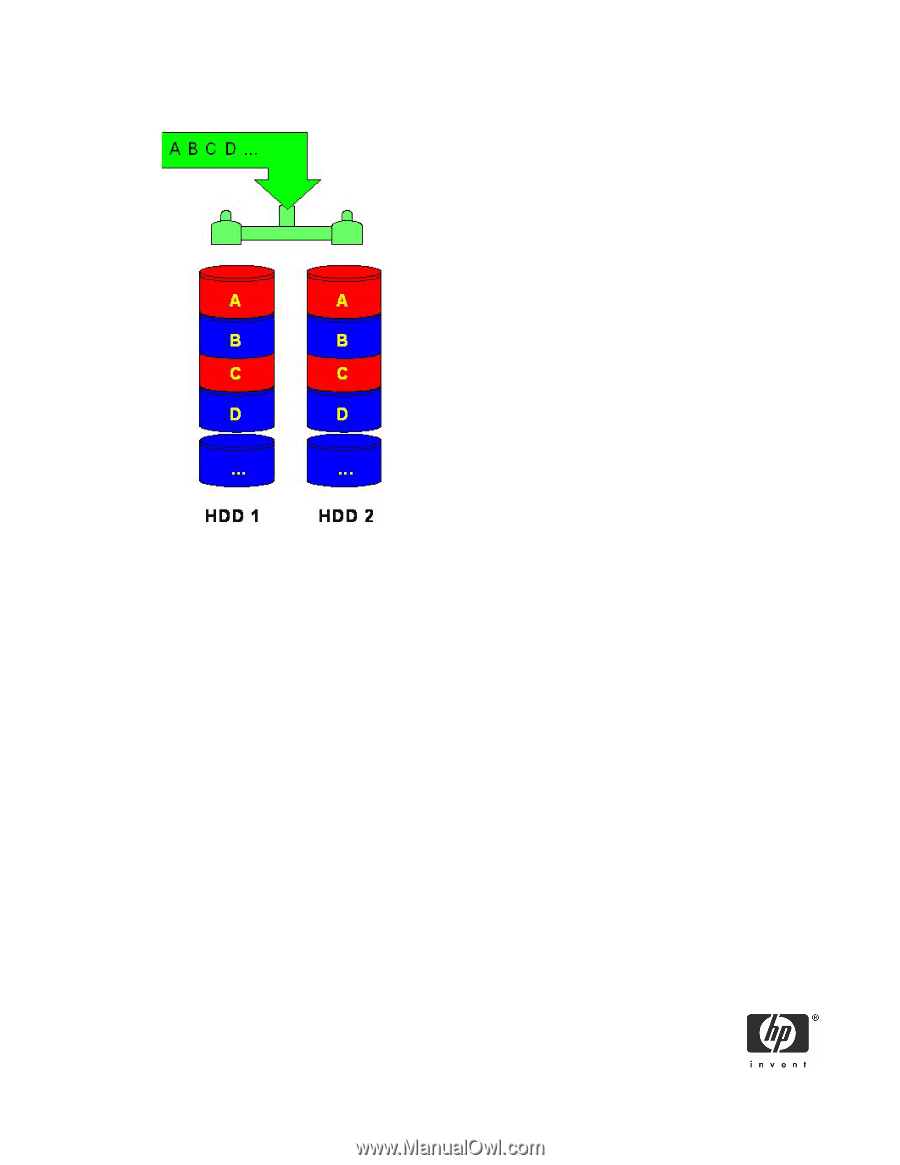
Figure 3
Reliability: RAID 1 - Mirroring
RAID 5 with three hard drives
RAID 5 has been used in servers for many years and is one of the most common types of RAID. RAID 5
uses striping with parity data in distributed blocks across all member disks. Therefore, the mass storage
controller can simultaneously write new information to two hard drives and parity information to the third
hard drive, so if one hard drive fails, the RAID controller can rebuild all the information after the volume
degradation occurred. Hence, RAID 5 with three hard drives has similar performance to RAID 0 with two
hard drives, and the reliability of RAID 1 with a minimum of three hard drives.