LG P930 Owner's Manual - Page 102
FCC Hearing-Aid, Compatibility HAC, Regulations for Wireless, Devices
 |
View all LG P930 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 102 highlights
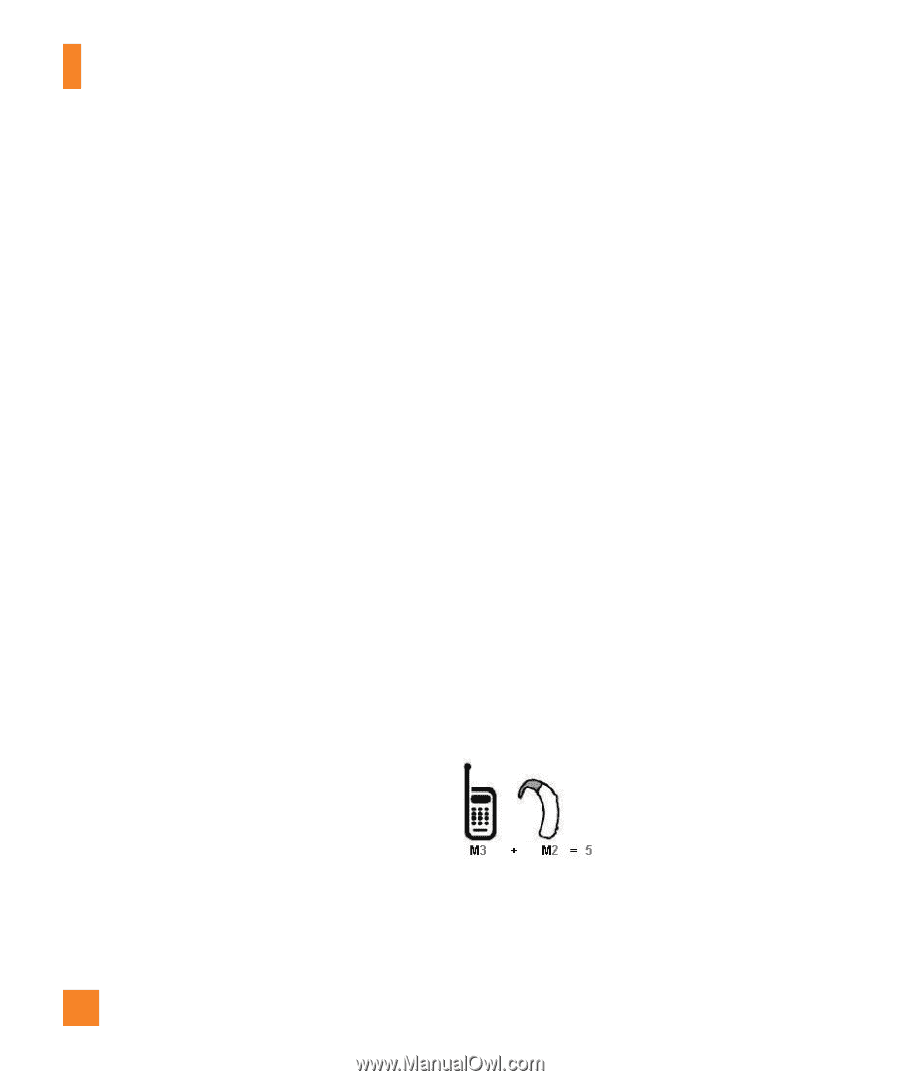
Safety Guidelines FCC Hearing-Aid Compatibility (HAC) Regulations for Wireless Devices On July 10, 2003, the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Report and Order in WT Docket 01-309 modified the exception of wireless phones under the Hearing Aid Compatibility Act of 1988 (HAC Act) to require digital wireless phones be compatible with hearing-aids. The intent of the HAC Act is to ensure reasonable access to telecommunications services for persons with hearing disabilities. While some wireless phones are used near some hearing devices (hearing aids and cochlear implants), users may detect a buzzing, humming, or whining noise. Some hearing devices are more immune than others to this interference noise, and phones also vary in the amount of interference they generate. The wireless telephone industry has developed a rating system for wireless phones, to assist hearing device users to find phones that may be compatible with their hearing devices. Not all phones have been rated. Phones that are rated have the rating on their box or a label located on the box. The ratings are not guarantees. Results will vary depending on the user's hearing device and hearing loss. If your hearing device happens to be vulnerable to interference, you may not be able to use a rated phone successfully. Trying out the phone with your hearing device is the best way to evaluate it for your personal needs. M-Ratings: Phones rated M3 or M4 meet FCC requirements and are likely to generate less interference to hearing devices than phones that are not labeled. M4 is the better/higher of the two ratings. Hearing devices may also be rated. Your hearing device manufacturer or hearing health professional may help you find this rating. Higher ratings mean that the hearing device is relatively immune to interference noise. The hearing aid and wireless phone rating values are then added together. A sum of 5 is considered acceptable for normal use. A sum of 6 is considered for best use. In the above example, if a hearing aid meets the M2 level rating and the wireless phone meets the M3 level rating, the sum of the two values equal 102