McAfee M-1250 IPS Configuration Guide - Page 182
Tunneled traffic, Small Fragment Threshold.
 |
View all McAfee M-1250 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 182 highlights
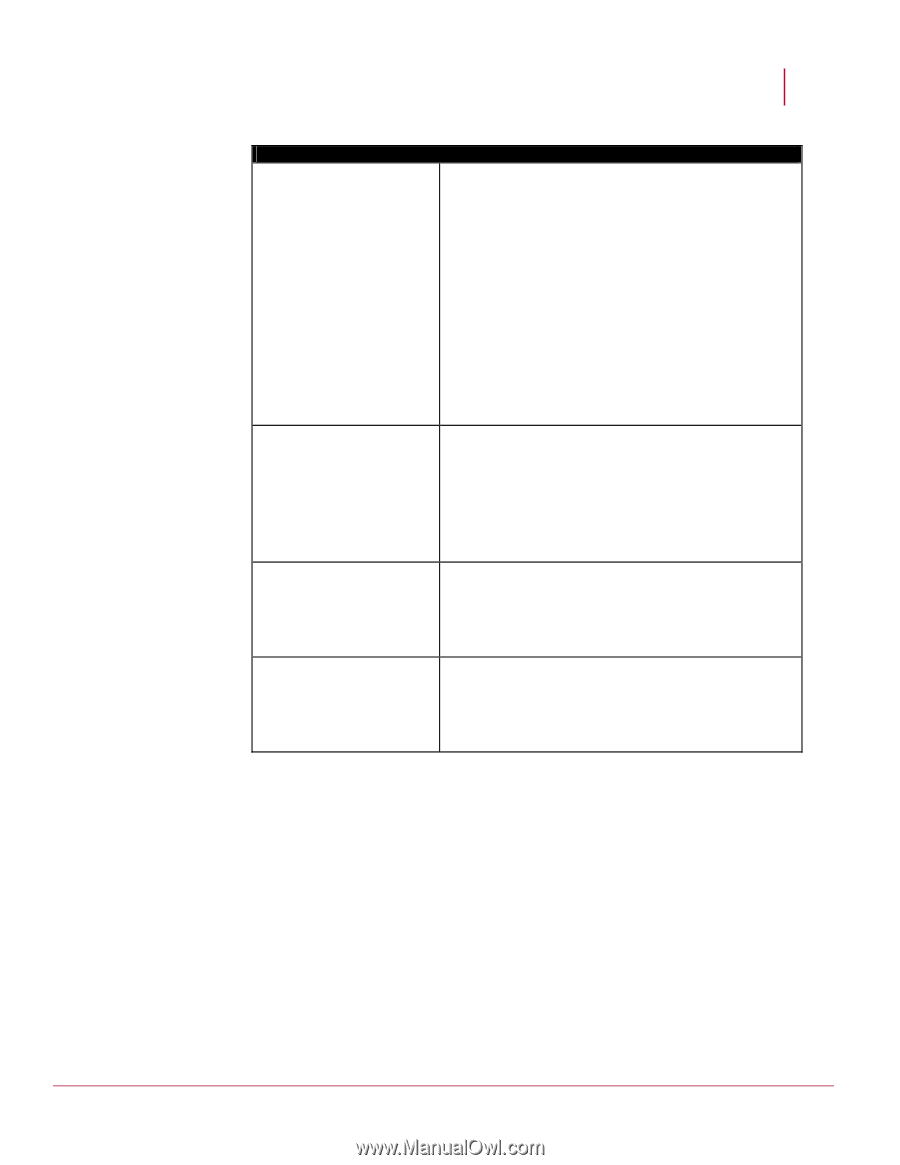
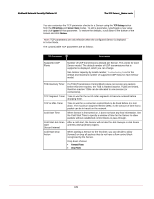
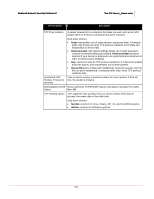
McAfee® Network Security Platform 5.1 The IPS Sensor_Name node IPv6 Scanning Overlap Option Smallest Fragment Size Small Fragment Threshold IPv6 Parameters Configuration Specify how the Sensor should process IPv6 traffic. • Drop all IPv6 traffic (inline only): The Sensor drops IPv6 traffic the inline mode. • Pass IPv6 traffic without scanning: The Sensor passes IPv6 packets but does not scan them for attacks. • Scan IPv6 traffic for attacks: The Sensor scans IPv6 traffic for attacks. If you select Scan IPv6 traffic for attacks or if you had selected this earlier and you are selecting a different option now, then you need to reboot the Sensor for the change to take effect. By default, IPv6 packets are not parsed but allowed to pass. You can check the IPv6 status of a Sensor using the status command from CLI. Fragmented IPv6 packets may overlap, thus you need to select which data to process first: the newer data or the older data. • Old Data: common for Windows and Solaris systems • New Data • Drop: The Sensor drops any overlapping fragments. By default, older data is processed first. Smallest allowable size for an IPv6 fragment to be seen as "normal." All IPv6 fragments under this size are counted toward the IPv6 Small Fragment Threshold. The default size is 48. You can modify this to a value which is a multiple of 8 and is between 40 and 1280. The number of IPv6 fragments under the IPv6 Smallest Fragment Size allowed in 60 seconds. If this threshold is exceeded, an alert is sent. The default is 10000. You can modify this to a value between 100 and 100,000. For IPv6 traffic, system events are generated for the following: • Reserved address where source or destination address is all zeros or 15 zeros then 1. • Final fragment with zero offset where next header = 44, fragment offset =0, and fragment header M = 0. You can view system events from the Threat Analyzer. For information on Threat Analyzer, see the System Status Monitoring Guide. Tunneled traffic This section describes how Network Security Platform handles tunneled traffic. IPv6 packets can pass through IPv4 networks when they are encapsulated in an IPv4 packet. By a similar way, IPv4 packets can also pass through IPv6 networks. This method of 174