McAfee M-1250 IPS Configuration Guide - Page 199
Configuring Traffic Management, in Enabling Traffic Management Settings
 |
View all McAfee M-1250 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 199 highlights
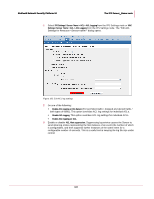
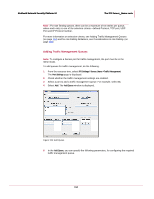
McAfee® Network Security Platform 5.1 The IPS Sensor_Name node Network Security Platform provides three different traffic management techniques- Rate limiting, DiffServ tagging and VLAN 802.1p tagging. Rate limiting is used to control the rate of traffic sent or received on a network interface. When deployed in the inline mode, Network Security Sensor provides rate limiting of traffic by limiting the bandwidth of the traffic that goes out of the Sensor port. Traffic that is less than or equal to the specified bandwidth value is allowed, whereas traffic that exceeds the bandwidth value is dropped. Network Security Sensor uses the token bucket approach for rate limiting traffic. Note: The token bucket is a control mechanism that specifies when the traffic can be transmitted, based on the presence of tokens in the bucket. Each token represents a unit of bytes. Differentiated services or DiffServ operates on the principle of traffic classification, where each data packet is classified and placed into a limited number of traffic classes. Each network device which supports DiffServ (for example, router), can be configured to differentiate traffic based on its class. So, you can manage each traffic class differently, ensuring preferential treatment for higher-priority traffic on the network. Network Security Sensor provides DiffServ tagging of packets. The tagged packets are used by DiffServ- compliant external network devices (such as routers) for traffic management. IEEE 802.1p specification enables network devices to prioritize traffic at the media access control (MAC) layer, and perform dynamic multi-cast filtering. The 802.1p header includes a three-bit field for prioritization, which allows packets to be grouped into various traffic classes. The three-bit prioritization field provides eight different classes of service to the user. The way the traffic is treated when assigned to any particular class is undefined, and left to the implementation. Network Security Sensor provides VLAN 802.1p tagging of packets, which are sent to VLAN 802.1p-compliant external network devices (for example, routers) for traffic management. Network Security Platform provides traffic management configuration at individual Sensor ports. That is, if 1A-1B is a port-pair, traffic management is configured separately for 1A and 1B. Traffic Management configuration for a port applies to the traffic going out of the port or egress traffic only. Note: Egress traffic is the network traffic that goes out of the monitoring port of the Sensor. Traffic management is applicable to Sensor ports in the inline mode only. In Manager, every traffic management queue of a Sensor is uniquely identified by a name. The traffic management queues are configured based on Protocol, TCP and UDP ports, and IP Protocol Number. For more information on adding different traffic management queues, see Adding Traffic Management Queues (on page 194). You can create multiple queues for each port of the Sensor. For more information on the number of queues that can be configured for each type of Sensor port (FE or GE), refer the section Queue Count in Enabling Traffic Management Settings (on page 192). The traffic management configuration in Manager must be followed by a configuration update to the Sensor. Configuring Traffic Management You can perform the following configuration tasks for traffic management, from Manager: 191