Belkin F5D6001_ver1 User Guide - Page 14
Encryption
 |
View all Belkin F5D6001_ver1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
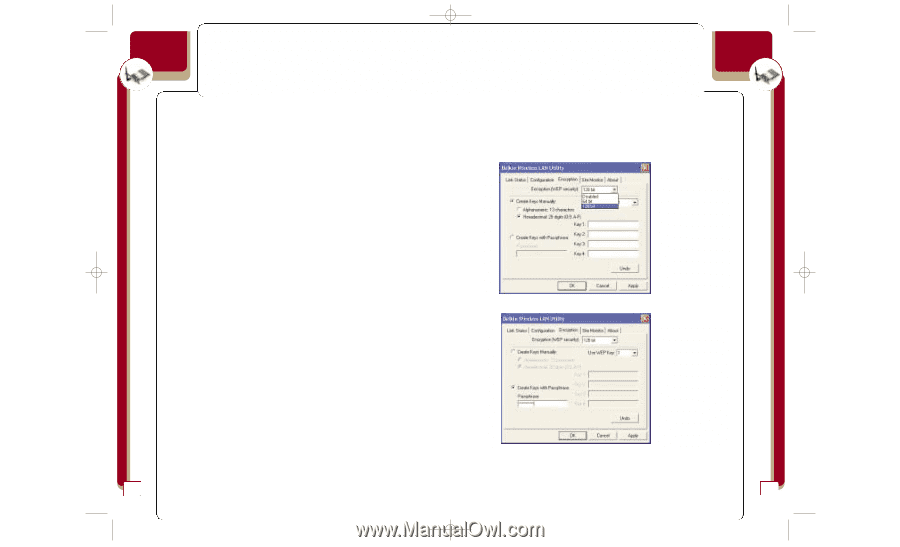
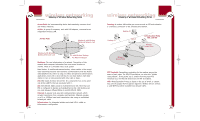
P74056_F5D6001_man(fp).qxd 5/3/2002 5:09 PM Page 22 wireless networking Encryption For security, the 802.11b standard incorporates a method of "scrambling" the data being sent over the air. This is called WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy). There are two different levels of WEP: 64-bit encryption and 128-bit encryption. 64-bit encryption is powerful and secure; 128-bit encryption is very powerful and very secure. The reason that two levels, or rates, of encryption exist is because encryption will slow the data speed down. The higher the rate of encryption, the slower the data will be transmitted. 64-bit encryption will reduce data rates nearly 30-40 percent where 128-bit encryption will reduce data rates around 50-60 percent. The trade-off is higher security for slower performance. Keep in mind, however, only large file transfers or continuous streaming data are most affected by this. Normal browsing of the Internet, downloading files, and sending and retrieving e-mails is not affected. How to Use Encryption Encryption is fairly easy to understand. Encryption uses what are called "keys" to encode and decode, or "scramble" and "unscramble", data. Keys can be made by entering a passphrase (password) or can be entered manually into the system using an alphanumeric series or a series of two-digit numbers (called "hexadecimal"). In Infrastructure mode, where an access point or wireless router is being used, the access point or wireless router is programmed with an encryption key. For a wireless device to join the wireless network, the same encryption key must be programmed into the device. Your Card can be programmed with a key in either the passphrase (easy) manner or with alphanumeric or hexadecimal (advanced) entries. wireless networking To Create an Encryption Key Using a Passphrase-EASY FOR NOVICE USERS 1. Click the "Encryption" tab. 2. Select the rate of encryption you need to use from the drop-down menu. 3. Select "Create Keys with Passphrase". 4. Type the network passphrase you need to use into the "Passphrase" box (for instance, "Passphrase"). 5. Click "Apply" to save the passphrase. 22 23