Belkin F5D6001_ver1 User Guide - Page 18
Glossary of Wireless Networking Terms
 |
View all Belkin F5D6001_ver1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
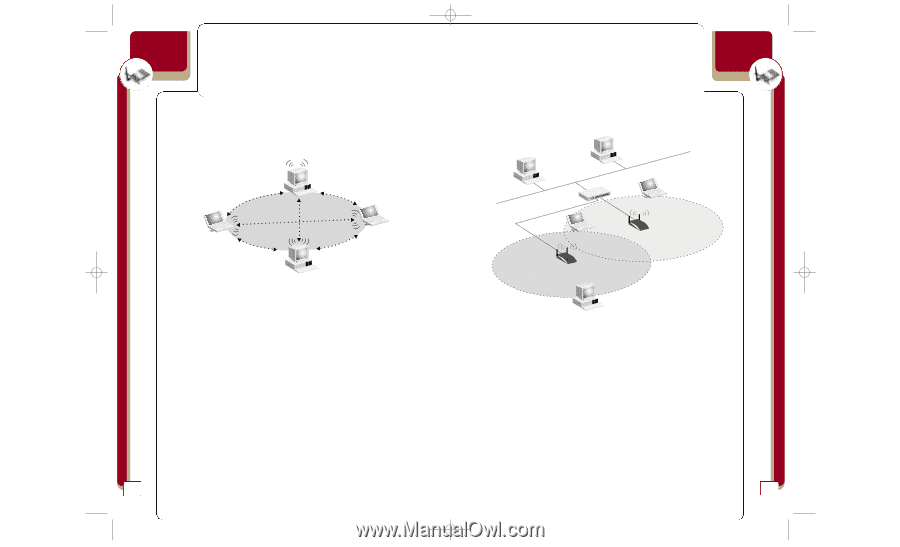
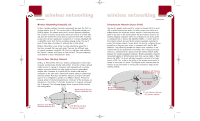
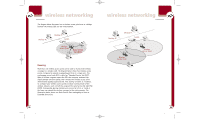
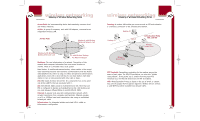
P74056_F5D6001_man(fp).qxd 5/3/2002 5:09 PM Page 30 wireless networking Glossary of Wireless Networking Terms Access Point: An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks. Ad-Hoc: A group of computers, each with LAN adapters, connected as an independent wireless LAN. Ad-Hoc Mode Notebook with Wireless Notebook Network Card Notebook with Wireless Notebook Network Card PC with Wireless Desktop PCI Network Adapter Backbone: The core infrastructure of a network. The portion of the network that transports information from one central location to another, where it is unloaded onto a local system. Base Station: In mobile telecommunications, a base station is the central radio transmitter/receiver that maintains communications with the mobile radio/telephone sets within its range. In cellular and personal communications applications, each cell or micro-cell has its own base station; each base station in turn is interconnected with other cells or bases. BSS: BSS stands for Basic Service Set. It is comprised of an access point and all the LAN PCs that are associated with it. ESS: ESS (ESS-ID, SSID) stands for Extended Service Set. More than one BSS is configured to become an Extended Service Set. LAN mobile users can roam between different BSSes in an ESS (ESS-ID, SSID). Ethernet: A popular local area data communications network, which accepts transmission from computers and terminals. Ethernet operates on a 10 or 100Mbps base band transmission rate, using an unshielded, twisted-pair cable. Infrastructure: An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure configuration. 30 wireless networking Glossary of Wireless Networking Terms Roaming: A wireless LAN mobile user moves around an ESS and maintains a continuous connection to the Infrastructure network. Desktop PC Desktop PC Switch Infrastructure Mode, BSS, and ESS Wireless Access Point BSS2 ESS Wireless Access Point BSS1 RTS Threshold: Transmitters contending for the medium may not be aware of each other. The RTS/CTS mechanism can solve this "hidden node problem". If the packet size is smaller than the preset RTS Threshold size, the RTS/CTS mechanism will NOT be enabled. WEP: Wired Equivalent Privacy is based on the use of 64-bit or 128-bit keys and the popular RC4 encryption algorithm. Wireless devices without a valid WEP key will be excluded from network traffic. 31