Dell S5248F-ON EMC SmartFabric OS10 Switch Configuration Guide for VxRail 4.7 - Page 15
Configuration planning
 |
View all Dell S5248F-ON manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
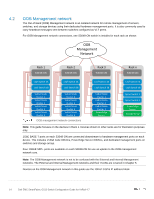
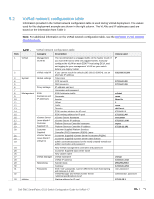
5 Configuration planning 5.1 VLANs and IP addresses VLANs and IP addresses used for VxRail node traffic must be planned before switch configuration and VxRail deployment can begin. VxRail node traffic is divided into five or more VLANs, as shown in Table 1. VLANs used for VxRail nodes VLAN Purpose External Management VxRail Manager, ESXi, vCenter Server, NTP, DNS, and vRealize Log Insight traffic vMotion Virtual machine (VM) migration vSAN Distributed storage traffic VM network(s) One or more VLANs for VM data traffic Internal Management VxRail node discovery Note: All VLANs in Table 1 share the physical connections shown in Chapter 3. VLAN configuration and IP network addresses planned for this deployment are shown in Table 2. VLAN IDs and IP addresses VLAN ID Description Network 1611 External Management 172.16.11.0/24 1612 vMotion 172.16.12.0/24 1613 vSAN 172.16.13.0/24 1614 VM Network A 172.16.14.0/24 1615 VM Network B 172.16.15.0/24 3939 Internal Management IPv6 multicast Gateway 172.16.11.254 NA NA Optional, not used Optional, not used not used VLAN ports Untagged Tagged Tagged Tagged Tagged Tagged Note: By default, VxRail does not enable routing of vSAN or vMotion traffic. This example uses two networks for VM data traffic, VM Network A and VM Network B, with each on a separate VLAN. The actual number of VM data networks used is based on customer requirements. The Internal Management VLAN, 3939, is used exclusively for VxRail node discovery using IPv6 multicast. Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping and querier must be enabled on this VLAN for node discovery to succeed. 15 Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 Switch Configuration Guide for VxRail 4.7