Icom IC-2820H Instruction Manual - Page 50
Repeater Operation
 |
View all Icom IC-2820H manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 50 highlights
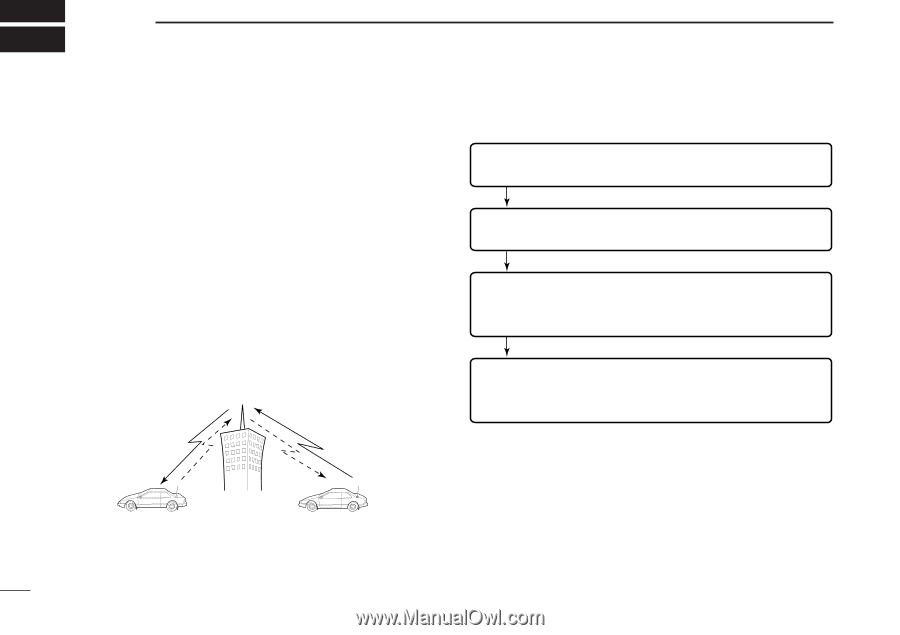
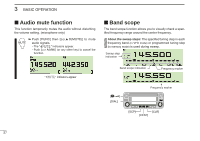
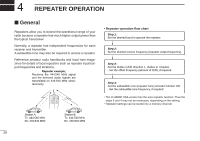
4 REPEATER OPERATION ■ General Repeaters allow you to extend the operational range of your radio because a repeater has much higher output power than the typical transceiver. Normally, a repeater has independent frequencies for each receiver and transmitter. A subaudible tone may also be required to access a repeater. Reference amateur radio handbooks and local ham magazines for details of local repeaters such as repeater input/output frequencies and locations. Repeater example; Receives the 444.540 MHz signal and the detected audio signals are transmitted on 449.540 MHz simultaneously. • Repeater operation flow chart Step 1: Set the desired band to operate the repeater. Step 2: Set the desired receive frequency (repeater output frequency). Step 3: Set the duplex (shift) direction (- duplex or +duplex). - Set the offset frequency (amount of shift), if required. Step 4: Set the subaudible tone (repeater tone) encoder function ON. - Set the subaudible tone frequency, if required. • The IC-2820H USA version has the auto repeater function. Thus the steps 3 and 4 may not be necessary, depending on the setting. • Repeater settings can be stored into a memory channel. Station A: Tx: 444.540 MHz Rx: 449.540 MHz Station B: Tx: 444.540 MHz Rx: 449.540 MHz 29