Intel AFCSASRISER User Guide - Page 32
Maximizing Performance, Table 10. RAID Levels and Performance
 |
View all Intel AFCSASRISER manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 32 highlights
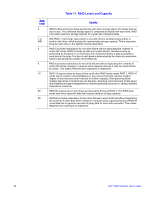
RAID Level Fault Tolerance 6 Combines distributed parity with disk striping. RAID 6 can sustain two drive failures and still maintain data integrity. Parity provides redundancy for two drive failures without duplicating the contents of entire disk drives. If a drive fails, the RAID controller uses the parity data to reconstruct all missing information. In RAID 6, this method is applied to entire drives or stripes across all drives in an array. Using distributed parity, RAID 6 offers fault tolerance with limited overhead. 10 Provides complete data redundancy using striping across spanned RAID 1 arrays. RAID 10 works well for any environment that requires the 100 percent redundancy offered by mirrored arrays. RAID 10 can sustain a drive failure in each mirrored array and maintain drive integrity. 50 Provides data redundancy using distributed parity across spanned RAID 5 arrays. RAID 50 includes both parity and disk striping across multiple drives. If a drive fails, the RAID controller uses the parity data to recreate all missing information. RAID 50 can sustain one drive failure per RAID 5 array and still maintain data integrity. 60 Provides data redundancy using distributed parity across spanned RAID 6 arrays. RAID 60 can sustain two drive failures per RAID 6 array and still maintain data integrity. It provides the highest level of protection against drive failures of all of the RAID levels. RAID 60 includes both parity and disk striping across multiple drives. If a drive fails, the RAID controller uses the parity data to recreate all missing information. Maximizing Performance A RAID disk subsystem improves I/O performance. The RAID array appears to the host computer as a single storage unit or as multiple virtual units. I/O is faster because drives can be accessed simultaneously. Table 10 describes the performance for each RAID level. Table 10. RAID Levels and Performance RAID Level Performance 0 RAID 0 (striping) offers the best performance of any RAID level. RAID 0 breaks up data into smaller blocks, then writes a block to each drive in the array. Disk striping writes data across multiple drives instead of just one drive. It involves partitioning each drive storage space into stripes that can vary in size from 8 KB to 128 KB. These stripes are interleaved in a repeated sequential manner. Disk striping enhances performance because multiple drives are accessed simultaneously. 1 or With RAID 1 or IME (mirroring), each drive in the system must be duplicated, which IME requires more time and resources than striping. Performance is impaired during drive rebuilds. 20 Intel® RAID Software User's Guide