RCA DRC8052N User Guide - Page 7
Explanation of Input Jacks and Cables - parts
 |
UPC - 840356939995
View all RCA DRC8052N manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 7 highlights
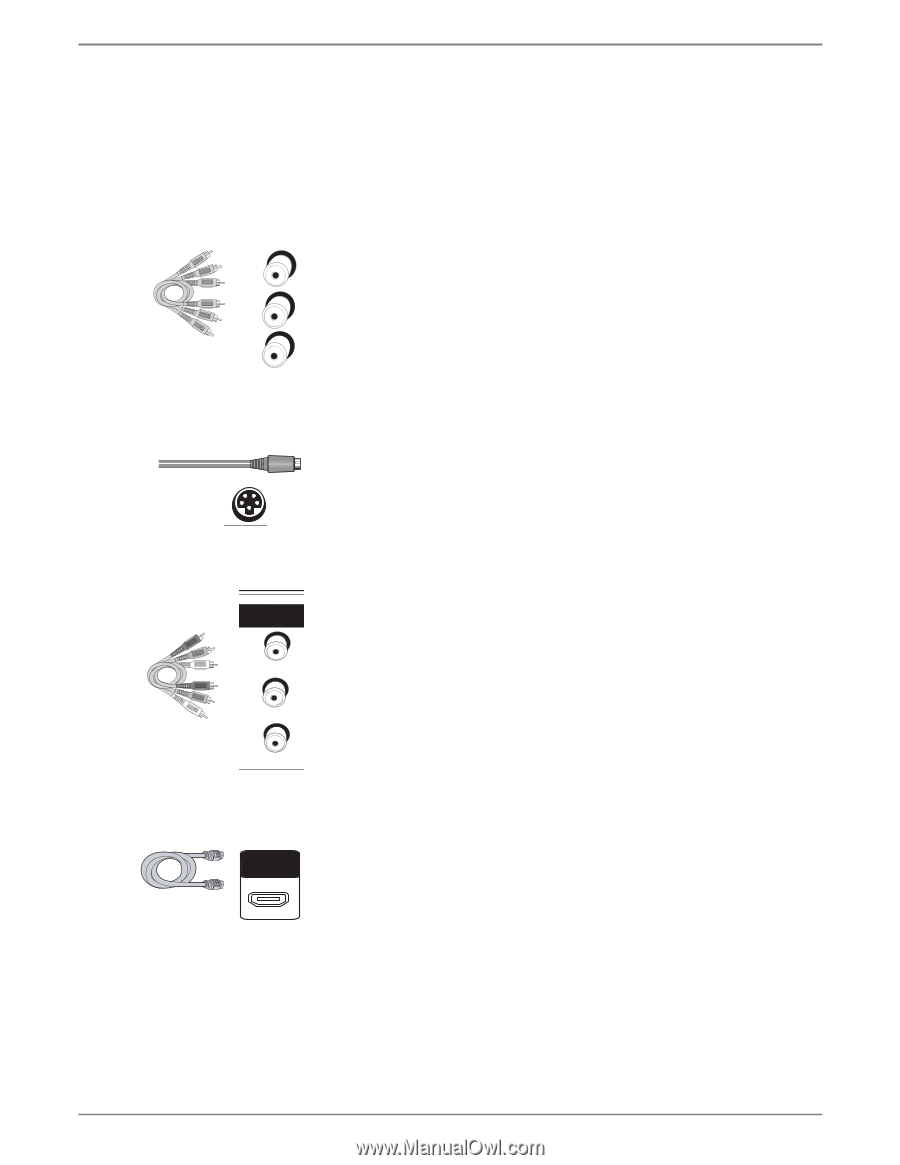
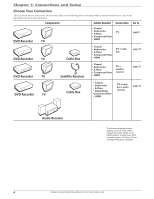
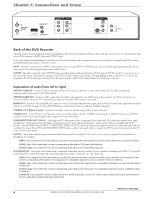
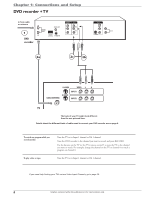
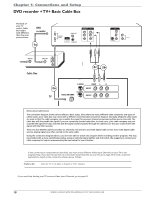
Chapter 1: Connections and Setup Explanation of Input Jacks and Cables This section describes the jacks and cables you can use to make connections. Some cables are supplied with your product or you can purchase other cables by calling 1-800-338-0376, order online at www.rca.com, or go to your local electronics store). There are several ways to connect your DVD recorder to your TV depending upon the cables you have and the jacks that are on the back of your TV. Different jacks and cables provide a different level of performance. It's important to remember, we're talking about degrees of picture improvement for comparison. If your TV has Component jacks (Y, Pb, Pr), S-VIDEO, and composite video (often color-coded yellow); Component (Y, Pb, Pr), would be considered excellent, S-Video would be very good, and the composite video jack (yellow) would be considered good. Y Pb Pr S AV1 IN VIDEO IN L R O IN HDMI OUT Component Video (Y, Pb, Pr) Jacks and Cables The Y, Pb, Pr jacks provide optimum picture quality because the video is separated into three signals (two signals are dedicated to the color portion of the image, and the other signal is dedicated to the black and white part of the image). To ensure maximum picture quality, use three video-grade cables (not supplied) for the connection. You can purchase bundled component video cables that are color-coded to match the Y, Pb, Pr jacks (red, green, and blue). Component Video Input jacks are usually found on high-end TVs, such as HDTVs; multimedia monitors; and some of the "flat" LCD and Plasma TVs or monitors. Notes: Also, remember to connect the left and right audio cables because the Y, Pb, Pr jacks and cables carry only the picture signal, not the sound. S-Video Jacks and Cables The S-Video (separate video) jack provides better picture quality than a composite video jack (sometimes labeled VIDEO and color-coded yellow on TVs) because S-Video keeps the color part of the picture separate from the black and white part of the picture. If your TV has an S-VIDEO jack, connect the DVD recorder to the TV with an S-Video cable for a better quality picture. Note: Remember to connect the left and right audio cables because the S-Video cable carries only the picture signal, not the sound. Audio/Video Jacks and Cables (RCA-type) Video The basic Video jack (usually color-coded yellow) is also referred to as composite video. Composite video doesn't keep color information separated (like S-Video), but it's better than the video quality you get from an RF coaxial cable (the type used to connect a cable signal or off-air antenna). Audio These jacks are used to send the audio from the disc you're playing in the DVD recorder to the TV. The audio jacks and cables (supplied) are often color-coded (red for right audio, and white for left audio). You must connect audio cables to the AUDIO L and R jacks on the DVD recorder and the corresponding Audio Input Jacks on the TV no matter which Video jack you connect (VIDEO; S-VIDEO; Y, Pb, Pr). Note: If your TV has only one input for audio (mono), connect it to the left (white) audio jack on the DVD recorder and don't connect the right (red) audio part of the cable. HDMI™ OUTPUT (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) Provides an uncompressed digital interface that carries both video and audio data to your TV by way of an integrated mini-plug cable (HDMI cable not supplied). When connected to a compatible high definition digital TV, the DVD recorder will convert standard definition signals to higher resolution (high definition) signals. Note: If your HDTV set has a DVI input and is HDCP (High Definition Copy Protection) compatible, you can connect your recorder to the TV using an optional HDMI cable and HDMI/DVI adapter. Remember to connect the left and right audio cables because the DVI cable carries only the picture signal, not the sound. Graphics contained within this publication are for representation only. 5