TP-Link T1600G-52PS TL-SG2452P T1600G-28PSTL-SG2424P V1 User Guide - Page 159
QoS
 |
View all TP-Link T1600G-52PS TL-SG2452P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 159 highlights
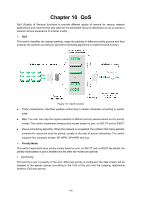
Chapter 10 QoS QoS (Quality of Service) functions to provide different quality of service for various network applications and requirements and optimize the bandwidth resource distribution so as to provide a network service experience of a better quality. QoS This switch classifies the ingress packets, maps the packets to different priority queues and then forwards the packets according to specified scheduling algorithms to implement QoS function. Figure 10-1 QoS function Traffic classification: Identifies packets conforming to certain characters according to certain rules. Map: The user can map the ingress packets to different priority queues based on the priority modes. This switch implements three priority modes based on port, on 802.1P and on DSCP. Queue scheduling algorithm: When the network is congested, the problem that many packets compete for resources must be solved, usually in the way of queue scheduling. The switch supports four schedule modes: SP, WRR, SP+WRR and Equ. Priority Mode This switch implements three priority modes based on port, on 802.1P and on DSCP. By default, the priority mode based on port is enabled and the other two modes are optional. 1. Port Priority Port priority is just a property of the port. After port priority is configured, the data stream will be mapped to the egress queues according to the CoS of the port and the mapping relationship between CoS and queues. 149