TP-Link TL-SG3210 TL-SG3210 V1 User Guide - Page 163
TP-Link TL-SG3210 Manual
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG3210 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 163 highlights
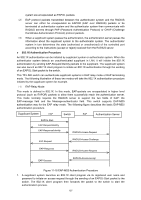
11.4 802.1X The 802.1X protocol was developed by IEEE802 LAN/WAN committee to deal with the security issues of wireless LANs. It was then used in Ethernet as a common access control mechanism for LAN ports to solve mainly authentication and security problems. 802.1X is a port-based network access control protocol. It authenticates and controls devices requesting for access in terms of the ports of LAN access control devices. With the 802.1X protocol enabled, a supplicant can access the LAN only when it passes the authentication, whereas those failing to pass the authentication are denied when accessing the LAN. ¾ Architecture of 802.1X Authentication 802.1X adopts a client/server architecture with three entities: a supplicant system, an authenticator system, and an authentication server system, as shown in the following figure. Figure 11-17 Architecture of 802.1X authentication (1) Supplicant System: The supplicant system is an entity in LAN and is authenticated by the authenticator system. The supplicant system is usually a common user terminal computer. An 802.1X authentication is initiated when a user launches client program on the supplicant system. Note that the client program must support the 802.1X authentication protocol. (2) Authenticator System: The authenticator system is usually an 802.1X-supported network device, such as this TP-LINK switch. It provides the physical or logical port for the supplicant system to access the LAN and authenticates the supplicant system. (3) Authentication Server System: The authentication server system is an entity that provides authentication service to the authenticator system. Normally in the form of a RADIUS server. Authentication Server can store user information and serve to perform authentication and authorization. To ensure a stable authentication system, an alternate authentication server can be specified. If the main authentication server is in trouble, the alternate authentication server can substitute it to provide normal authentication service. ¾ The Mechanism of an 802.1X Authentication System IEEE 802.1X authentication system uses EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) to exchange information between the supplicant system and the authentication server. (1) EAP protocol packets transmitted between the supplicant system and the authenticator 156