Yamaha PSR-S900 Owner's Manual - Page 203
What You Can Do With MIDI, MIDI Data Compatibility, System Messages, Sequence Formats - problems
 |
View all Yamaha PSR-S900 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 203 highlights
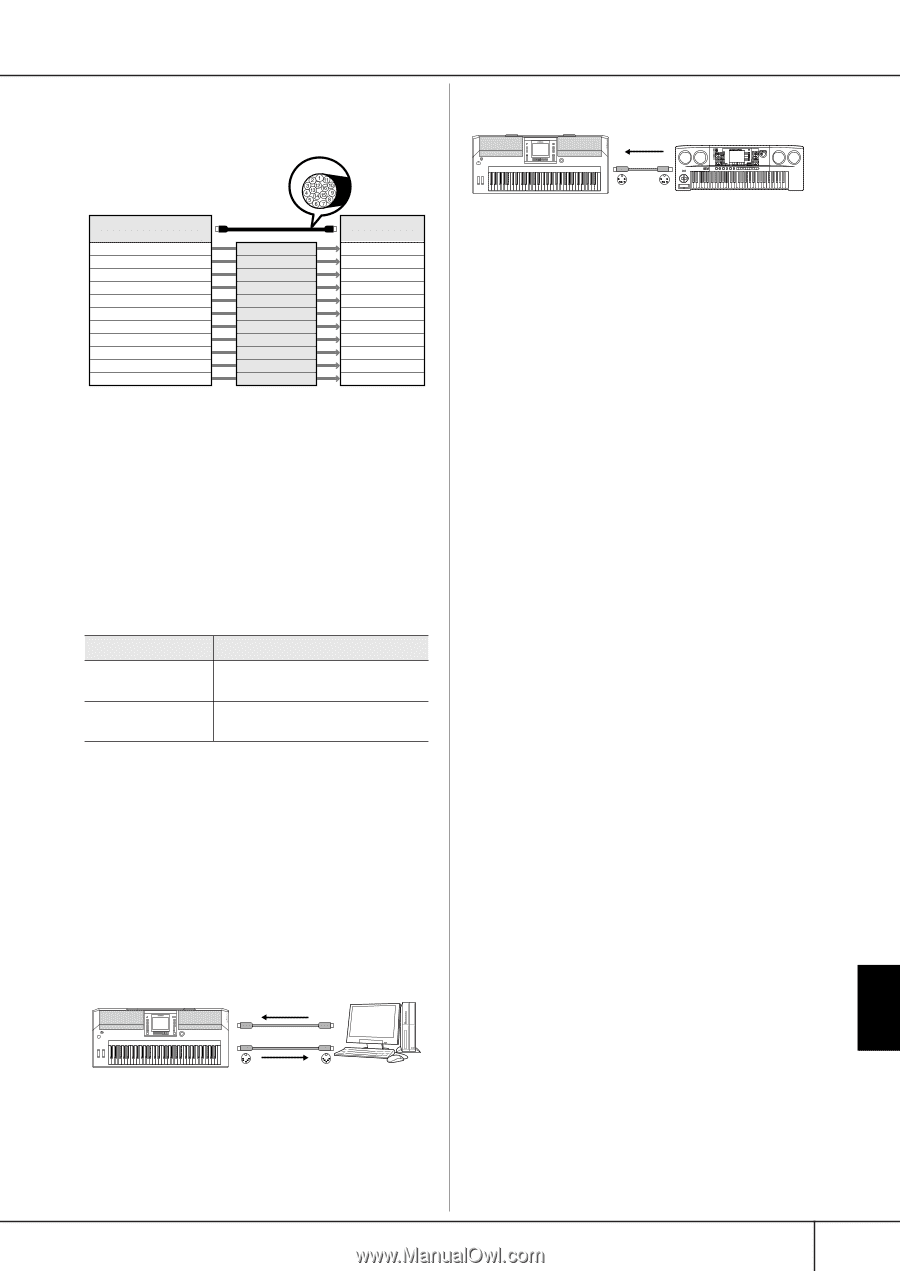
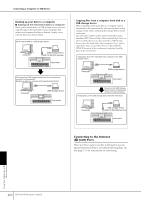
What is MIDI? Example: Recording a performance with the auto accompaniment (Style playback) sound of the instrument to an external sequencer PSR-S900/S700 track (channel) RIGHT 1 RIGHT 2 LEFT STYLE instrument STYLE instrument STYLE instrument STYLE instrument STYLE instrument STYLE instrument STYLE instrument STYLE instrument MIDI cable Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3 Channel 4 Channel 5 Channel 6 Channel 7 Channel 8 Channel 9 Channel 10 Channel 11 External sequencer Track 2 Track 3 Track 4 Track 5 Track 6 Track 7 Track 8 Track 9 Track 10 Track 11 As you can see, it is essential to determine which data is to be sent over which MIDI channel when transmitting MIDI data (page 207). The instrument also allows you to determine how the received data is played back (page 208). System Messages This is data that is used in common by the entire MIDI system. These include System Exclusive messages for transferring data unique to each instrument manufacturer and Realtime messages for controlling the MIDI device. Message Name Operation/Panel Setting System Exclusive Message Effect type settings (Mixing Console), etc. Realtime Messages Clock setting, Start/stop operation The messages transmitted/received by the PSR-S900/ S700 are shown in the MIDI Data Format and MIDI Implementation Chart in the Data List. The Data List is available at the Yamaha website. (See page 5.) What You Can Do With MIDI ■ Record your performance data (1-16 channels) using the auto accompaniment features on an external sequencer (or computer with sequencer software). After recording, edit the data with the sequencer, then play it back on the instrument. MIDI receive MIDI IN MIDI OUT MIDI OUT MIDI IN Instrument MIDI transmit Computer or Sequencer When you want to use the instrument as an XG-compatible multi-timbral tone generator, set the receive part for MIDI channels 1-16 to "SONG" in MIDI/USB 1 in MIDI Receive (page 208). ■ Controlling from an external MIDI keyboard MIDI receive MIDI IN MIDI OUT Instrument MIDI Data Compatibility This section covers basic information on data compatibility: whether or not other MIDI devices can playback the data recorded by PSR-S900/S700, and whether or not the PSR-S900/S700 can playback commercially available song data or song data created for other instruments or on a computer. Depending on the MIDI device or data characteristics, you may be able to play back the data without any problem, or you may have to perform some special operations before the data can be played back. If you run into problems playing back data, please refer to the information below. Sequence Formats Song data is recorded and stored in a variety of different systems, referred to as "sequence formats." Playback is only possible when the sequence format of the Song data matches that of the MIDI device. The PSR-S900/S700 is compatible with the following formats. ● SMF (Standard MIDI file) This is the most common sequence format. Standard MIDI Files are generally available as one of two types: Format 0 or Format 1. Many MIDI devices are compatible with Format 0, and most commercially available software is recorded as Format 0. • The PSR-S900/S700 is compatible with both Format 0 and Format 1. • Song data recorded on the PSR-S900/S700 is auto- matically saved as SMF Format 0. ● ESEQ This sequence format is compatible with many of Yamaha's MIDI devices, including the PSR-S900/S700 series instruments. This is a common format used with various Yamaha software. • The PSR-S900/S700 is compatible with ESEQ. ● XF The Yamaha XF format enhances the SMF (Standard MIDI File) format with greater functionality and openended expandability for the future. The PSR-S900/S700 is capable of displaying lyrics when an XF file containing lyric data is played. (SMF is the most common format used for MIDI sequence files. The PSR-S900/S700 is compatible with SMF Formats 0 and 1, and records "song" data using SMF Format 0.) ● Style File The Style File Format (SFF) combines all of Yamaha's auto accompaniment know-how into a single unified format. Using Your Instrument with Other Devices PSR-S900/S700 Owner's Manual 203