ZyXEL G-160 User Guide - Page 25
Wireless LAN Security, RTS Threshold
 |
View all ZyXEL G-160 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 25 highlights
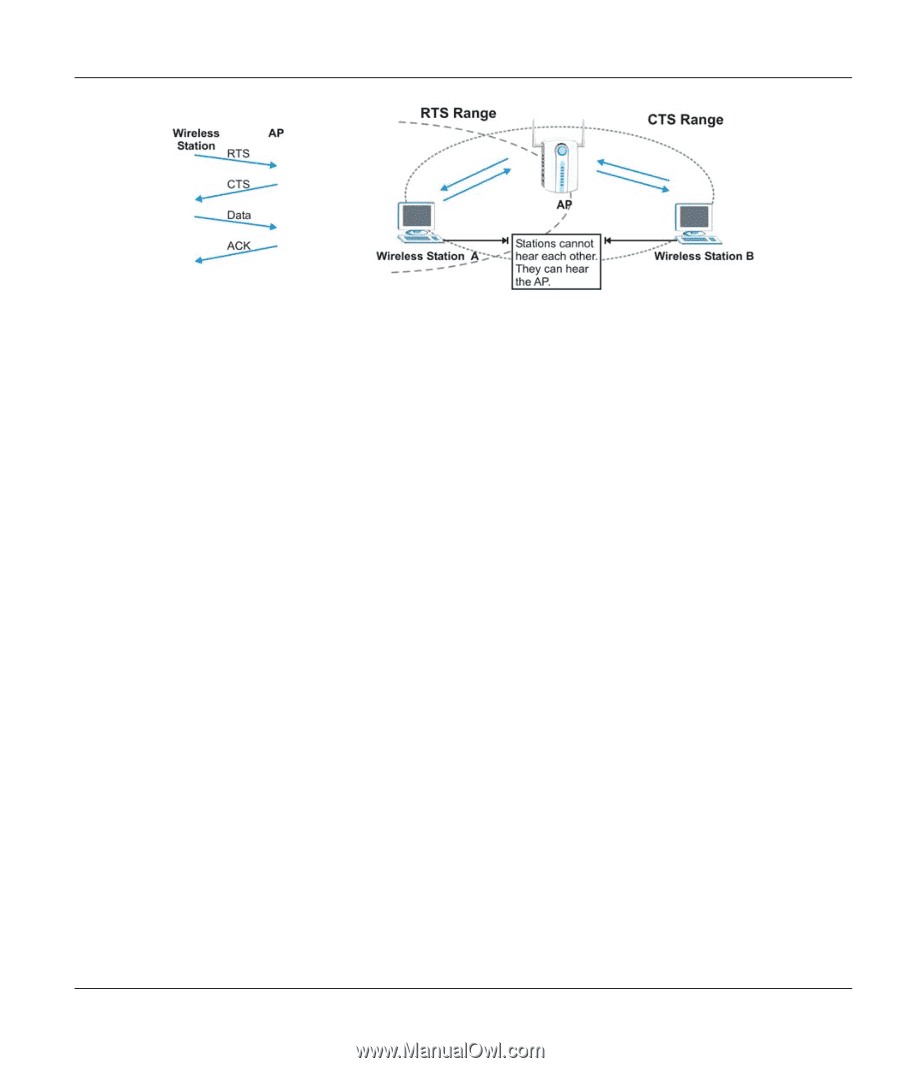
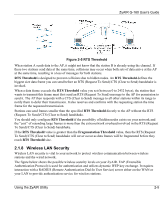
ZyAIR G-160 User's Guide Figure 2-5 RTS Threshold When station A sends data to the AP, it might not know that the station B is already using the channel. If these two stations send data at the same time, collisions may occur when both sets of data arrive at the AP at the same time, resulting in a loss of messages for both stations. RTS Threshold is designed to prevent collisions due to hidden nodes. An RTS Threshold defines the biggest size data frame you can send before an RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake is invoked. When a data frame exceeds the RTS Threshold value you set (between 0 to 2432 bytes), the station that wants to transmit this frame must first send an RTS (Request To Send) message to the AP for permission to send it. The AP then responds with a CTS (Clear to Send) message to all other stations within its range to notify them to defer their transmission. It also reserves and confirms with the requesting station the time frame for the requested transmission. Stations can send frames smaller than the specified RTS Threshold directly to the AP without the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake. You should only configure RTS Threshold if the possibility of hidden nodes exists on your network and the "cost" of resending large frames is more than the extra network overhead involved in the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake. If the RTS Threshold value is greater than the Fragmentation Threshold value, then the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake will never occur as data frames will be fragmented before they reach RTS Threshold size. 2.1.8 Wireless LAN Security Wireless LAN security is vital to your network to protect wireless communication between wireless stations and the wired network. The figure below shows the possible wireless security levels on your ZyAIR. EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) is used for authentication and utilizes dynamic WEP key exchange. It requires interaction with a RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) server either on the WAN or your LAN to provide authentication service for wireless stations. Using the ZyAIR Utility 2-5