ZyXEL G-162 User Guide - Page 85
D. Wireless LANs
 |
View all ZyXEL G-162 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 85 highlights
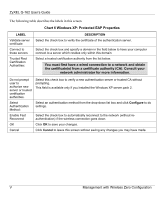
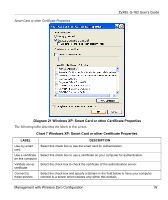
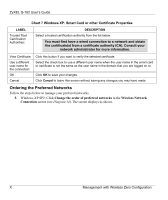
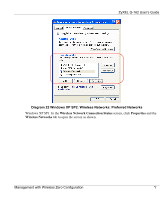
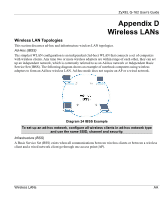
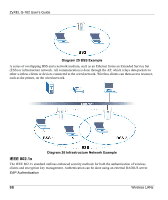
ZyXEL G-162 User's Guide Appendix D Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topologies This section discusses ad-hoc and infrastructure wireless LAN topologies. Ad-Hoc (IBSS) The simplest WLAN configuration is an independent (Ad-hoc) WLAN that connects a set of computers with wireless clients. Any time two or more wireless adapters are within range of each other, they can set up an independent network, which is commonly referred to as an Ad-hoc network or Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS). The following diagram shows an example of notebook computers using wireless adapters to form an Ad-hoc wireless LAN. Ad-hoc mode does not require an AP or a wired network. Diagram 24 IBSS Example To set up an ad-hoc network, configure all wireless clients in ad-hoc network type and use the same SSID, channel and security. Infrastructure (BSS) A Basic Service Set (BSS) exists when all communications between wireless clients or between a wireless client and a wired network client go through one access point (AP). Wireless LANs AA