ZyXEL G-162 User Guide - Page 89
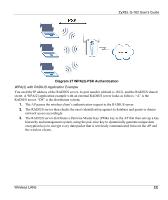
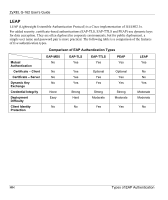
Diagram 27 WPA2-PSK Authentication, ZyXEL G-162 User's Guide, Wireless LANs - ee
 |
View all ZyXEL G-162 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 89 highlights
ZyXEL G-162 User's Guide Diagram 27 WPA(2)-PSK Authentication WPA(2) with RADIUS Application Example You need the IP address of the RADIUS server, its port number (default is 1812), and the RADIUS shared secret. A WPA(2) application example with an external RADIUS server looks as follows. "A" is the RADIUS server. "DS" is the distribution system. 1. The AP passes the wireless client's authentication request to the RADIUS server. 2. The RADIUS server then checks the user's identification against its database and grants or denies network access accordingly. 3. The RADIUS server distributes a Pairwise Master Key (PMK) key to the AP that then sets up a key hierarchy and management system, using the pair-wise key to dynamically generate unique data encryption keys to encrypt every data packet that is wirelessly communicated between the AP and the wireless clients. Wireless LANs EE