Compaq ProLiant 1000 I/O Performance Tuning of Compaq Servers - Page 13
Fibre Channel Bandwidth & Saturation, Distance and Arbitration Issues
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 13 highlights
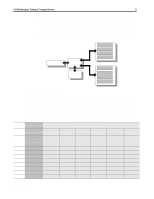
I/O Performance Tuning of Compaq Servers 13 capable of transmitting 100 MB/s over tremendous distances. Fibre Channel can be deployed using many topologies. Fibre Channel Bandwidth & Saturation Similar to the SCSI and PCI busses, a Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop (FC-AL) can become saturated and limit performance. Since FC bus can carry 100 MB/s, saturating the FC bus would require at least two Fibre Channel Arrays, delivering greater than 50MB/s each. Compaq Fibre Channel Arrays are dedicated storage enclosures with integrated SMART-2 technology, each array can deliver a theoretical maximum of 80 MB/s. Here again, knowing the loads placed on your server provides insight to the number of devices that would saturate your Fibre Channel. In practice, only when operating in the most I/O stressful environments would the FC-AL become saturated. For example, in order to saturate the FC loop, you would need to have three simultaneous, broadcast-quality video streams on the FC. If you operate your server under such extreme I/O conditions, you should install additional Fibre Channel Controllers to provide another 100 MB/s pathway to your storage. If you use multiple Fibre Channel loops, you should try to balance the I/O load between the loops. However, balancing the loads may provide only marginal performance improvements unless one loop has consistently high utilization. Distance and Arbitration Issues Compaq Fibre Channel technology allows greater distance than any other storage bus. However, as the distances between server and storage, and storage and hub become several kilometers, the delay introduced by the data traversing the bus becomes noticeable. The delay, caused by data travelling at the speed of light, cannot be eliminated. By understanding the source of the delay, you can better implement distant storage for your server. Compaq Fibre Channel Array 5 Server Compaq Fibre Channel Array 0 Compaq Fibre Channel Array 4 Fibre Channel Storage Hub 7 Compaq Fibre Channel Array 1 Compaq Fibre Channel Array 3 Compaq Fibre Channel Array 2 Figure 4. Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop Topology 10km 140km ECG044.0399