Compaq ProLiant 1000 I/O Performance Tuning of Compaq Servers - Page 6
Peripheral Component Interconnect PCI Bus
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 6 highlights
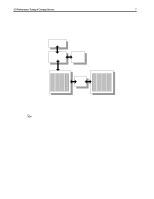
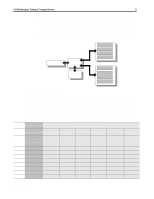
I/O Performance Tuning of Compaq Servers 6 great deal of write requests. In each of these situations, tuning the performance of the server requires a different approach. As a result, knowing the kind of load, or server mix, that clients place on your server is key to tuning your I/O. On most local area networks, servers are connected to clients over an Ethernet network. Currently, there are three Ethernet specifications: • 10BASE-T provides each client with a shared resource with a maximum bandwidth of 10 Megabits per second (Mb/s) or 1 Megabyte per second (MB/s). • 100BASE-T is 10 times faster than 10BASE-T, providing 10 MB/s of bandwidth. • Gigabit Ethernet, the newest specification, can move approximately 120 MB of data per second; 100 times faster than the original 10BASE-T specification. Ideally, the server should be able to deliver the full 1 MB/s, 10 MB/s, or 100 MB/s to every network segment, depending on the NICs used. In practice, however, on multi-client networks with unswitched hubs and repeaters each client shares the bandwidth resource with all other clients on the segment. To overcome this limitation, intelligent network switches enable point to point communication between nodes. When using network switches, each port on the switch is seen as the only client on that network segment. In this case, your network maximizes throughput because collisions are eliminated. Switches allow greater utilization of bandwidth, however the added cost of intelligent switches may outweigh the performance gains in smaller, less stressed network segments. P When planning or implementing your network, be aware of utilization limitations. Either distribute network traffic between separate network segments or use intelligent switches to eliminate packet collisions and maximize throughput. Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Bus The PCI bus is a high-performance, 32 or 64-bit local bus that provides an interface for highspeed transfers to peripheral components without taxing the host processor. A single 32-bit PCI bus provides 133 MB/s of bandwidth between PCI devices and the host bus, which holds the CPU and main memory. In order to provide greater performance and connectivity, Compaq ProLiant servers (models 1200 to 7000) use a bridged-PCI architecture to connect multiple PCI busses within the server. Compaq uses two different architectures to connect the two PCI busses to the host bus: the dual-peer PCI bus and the bridged PCI bus. P In order to maintain maximum performance, Compaq recommends that you balance the load according to the architecture in your server. Bus Balancing in ProLiant Servers Bridged PCI bus P In bridged PCI busses, such as the ProLiant 2500 and ProLiant 2500R, you should populate the primary PCI bus completely before adding any adapters to the secondary bus. Because the secondary PCI bus shares the data path of the primary PCI bus, bus balancing is not recommended in bridged-PCI servers. In fact, Compaq recommends that you have the primary bus completely populated before adding cards to the secondary bus. Cards in the secondary bus need to pass their control and data through the extra bridge chip and incur delays not only from ECG044.0399