Compaq ProLiant 1000 I/O Performance Tuning of Compaq Servers - Page 29
Write caching is
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
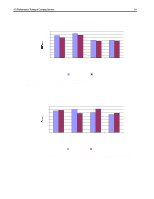
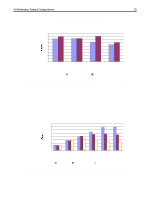
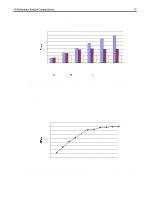
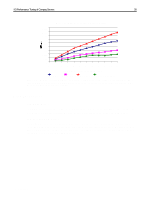
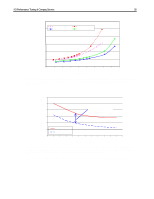
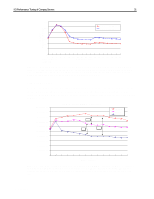
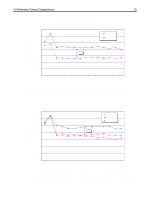
I/O Performance Tuning of Compaq Servers 29 I/Os per second Sequential Read: 2% Sequential Write: 1% 1400 Composite Performance Random Read: 58% Random Write: 39% 1200 1000 Representative Compaq 7,200-rpm drive Compaq 10k-II drive 800 600 400 200 With larger block sizes, the SCSI bus will saturate, limiting the I/O rate 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Number of Drives/Block Count Figure 17. Composite performance of 10k-II drives and 7,200-rpm drives in a typical server environment. These results were obtained using Iometer version 1998.10.08, Copyright 1998 by Intel Corporation. Intel does not endorse any Iometer results. In Figure 17, the x-axis indicates the number of drives on the SCSI bus. The eight marks between each number indicate the number of blocks transferred in a single input/output (I/O) (1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128 blocks of data, respectively). One block is 512 bytes. Write caching is disabled. Queuing is simple with 16 tagged commands. Percentage/Scaled (based-10k)/base Composite Performance Sequential Read: 2% Sequential Write: 1% Random Read: 58% Random Write: 39% 50 40 30 20 Representative Compaq 7,200-rpm drive Compaq 10k-II drive 10 0 -10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Number of Drives/Block Count Figure 18. Percent improvement calculated using values from Figure 17. These results were obtained using Iometer version 1998.10.08, Copyright 1998 by Intel Corporation. Intel does not endorse any Iometer results. Figures 19 and 20 illustrate the additional performance gains associated with 10K RPM drives. Figure 19 shows the decrease in latency for both read and write operations.While Figure 20 exhibits the increased throughput for client requests. ECG044.0399