Compaq ProLiant 1000 I/O Performance Tuning of Compaq Servers - Page 18
System Memory
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
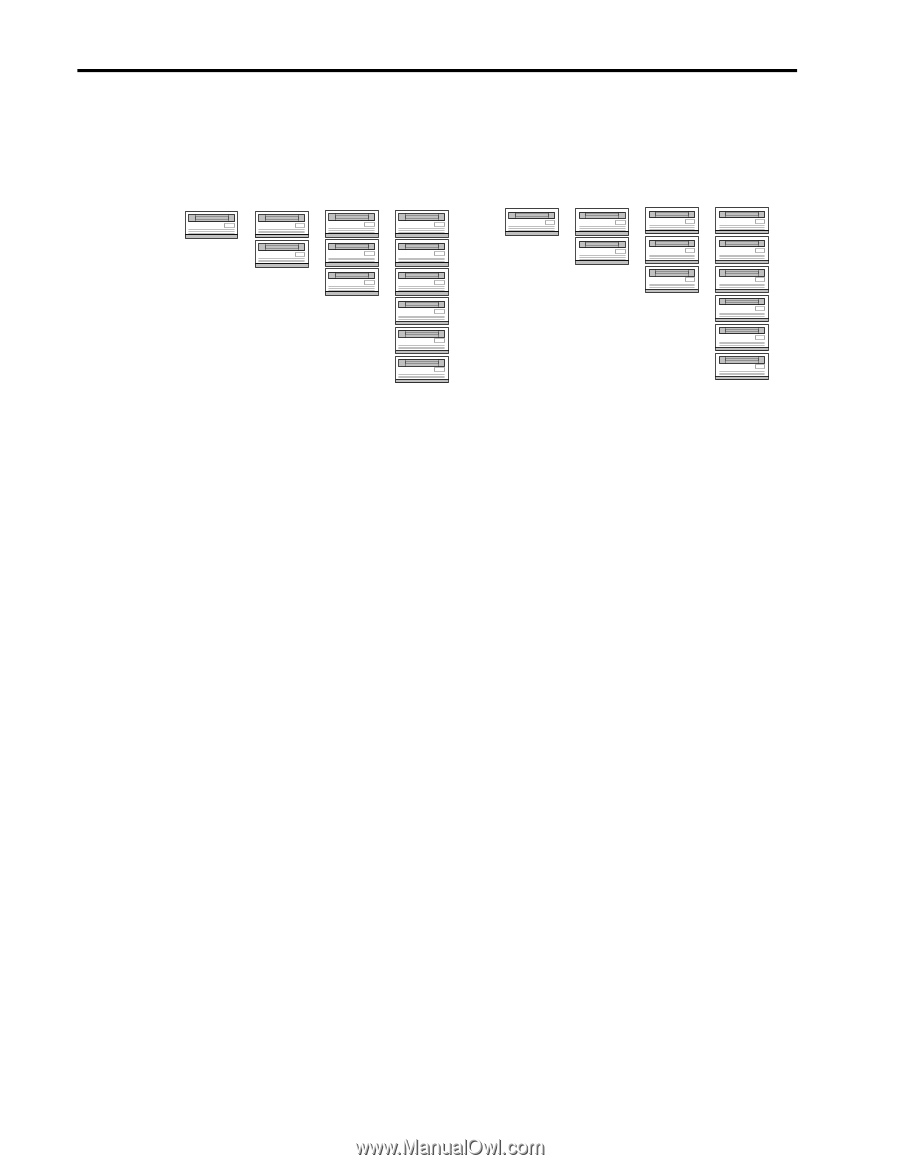
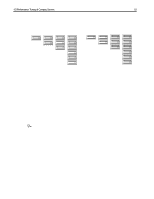
I/O Performance Tuning of Compaq Servers 18 As mentioned, spanning your data across more drives gives a case of increased performance with diminishing returns. Compaq has found that adding drives to an array provides greater throughput regardless of storage capacity and fault tolerance level. This is true for both like drive and like 18GB 18GB 18GB 18GB 2GB 4GB 6GB 12GB 1 - 18GB drive 2 - 9GB drives 3 - 6GB drives 1 - 2GB drive 2 - 2GB drives 3 - 2GB drives Like Capacity Scaling Figure 6. Drive Scaling Schemes 6 - 3GB drives Like Drive Scaling 6 - 2GB drives capacity scaling. The danger of using many small drives to reach your storage requirements is that you limit the maximum amount of storage that would be available on that SCSI bus. If you had filled a Fibre Channel Array with twelve, 2 GB drives to maximize the number of spindles, and, in turn, performance, there would be no free drive slots in the array for future expansion. Using six, 4 GB storage would provide you with the same 24 GB of storage as well as six open slots in your Fibre Channel Array chassis. However, the six-drive configuration would not respond as quickly to random, small-block transfers. Another factor to consider is cost. In most cases, it costs less to implement the same capacity with more drives, until you reach a point that more chassises are required to hold too many of the smaller drives. Newer technology disk drives are usually faster and smaller with greater storage area, but cost a premium. Disk technologies and drive costs are changing so fast that making specific recommendations is difficult. Choose carefully the parameters you want to maximize for your system: costs, performance, capacity, replaceability, or future expandability. Saving money now, may cost more in the future when the failed drive becomes harder to find. P It is up to you to determine which type of drive scaling is right for your server's workload. More random, small-block transfers enjoy greater performance benefits with more spindles. On the other hand, large, sequential transfer environments show decreasing gains much sooner when scaling by adding drives. In addition to adding drives, adding controllers may provide significant performance gains in certain environments. Since fault-tolerant RAID requires parity calculations for all data written to the drives, dividing this load between redundant hardware can, once again, provide increased throughput, especially in RAID 5. Redundant controllers provide little or no gains;roughly 3%, for lower RAID levels that do not use parity information. Conversely, a RAID 5 system can realize up to a 57% increase in throughput when parity generation is assisted by a second controller. As usual, knowing your server setup and RAID level implemented will help you weigh the performance gains against the added cost of the second controller card. System Memory Even the most optimized server can improve response time to client requests by adding additional system memory. Since server operating systems employ powerful caching algorithms, client ECG044.0399