D-Link DSN-6110 User Manual for DSN-6110 & DSN-6110 with DSN-610 - Page 11
iSCSI concepts
 |
View all D-Link DSN-6110 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
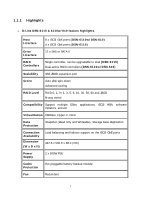
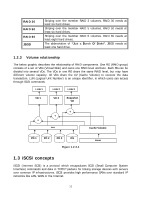
RAID 30 RAID 50 RAID 60 JBOD Striping over the member RAID 3 volumes. RAID 30 needs at least six hard drives. Striping over the member RAID 5 volumes. RAID 50 needs at least six hard drives. Striping over the member RAID 6 volumes. RAID 60 needs at least eight hard drives. The abbreviation of "Just a Bunch Of Disks". JBOD needs at least one hard drive. 1.2.3 Volume relationship The below graphic describes the relationship of RAID components. One RG (RAID group) consists of a set of VDs (Virtual Disk) and owns one RAID level attribute. Each RG can be divided into several VDs. The VDs in one RG share the same RAID level, but may have different volume capacity. All VDs share the CV (Cache Volume) to execute the data transaction. LUN (Logical Unit Number) is an unique identifier, in which users can access through SCSI commands. LUN 1 LUN 2 LUN 3 VD 1 VD 2 Snapshot VD + + + RG Cache Volume PD 1 PD 2 PD 3 DS Figure 1.2.3.1 RAM 1.3 iSCSI concepts iSCSI (Internet SCSI) is a protocol which encapsulates SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) commands and data in TCP/IP packets for linking storage devices with servers over common IP infrastructures. iSCSI provides high performance SANs over standard IP networks like LAN, WAN or the Internet. 11